An inside look at Quaker culture and traditions most people don’t know
Welcome to the intriguing world of the Quakers, a religious group known for its unique approach to faith and community. With a history rich in innovation and social impact, the Quakers have left an indelible mark on the world.
But who are they, really? In this article, we’ll unravel the mystery of the Quakers, exploring their beliefs, history, and contributions to society. Join us as we delve into the fascinating journey of this spirited group.
Who Are the Quakers? A Brief Overview

The Quakers, formally known as the Religious Society of Friends, are a Christian denomination founded in the 17th century. They are best known for their commitment to peace, simplicity, and equality.
Unlike many religious groups, Quakers have no clergy or formal liturgy, emphasizing personal experience and direct communion with God. Their meetings are often silent, allowing individuals to speak as they feel led. This unique structure fosters a deep sense of community and shared purpose.
The Origins of the Quaker Movement

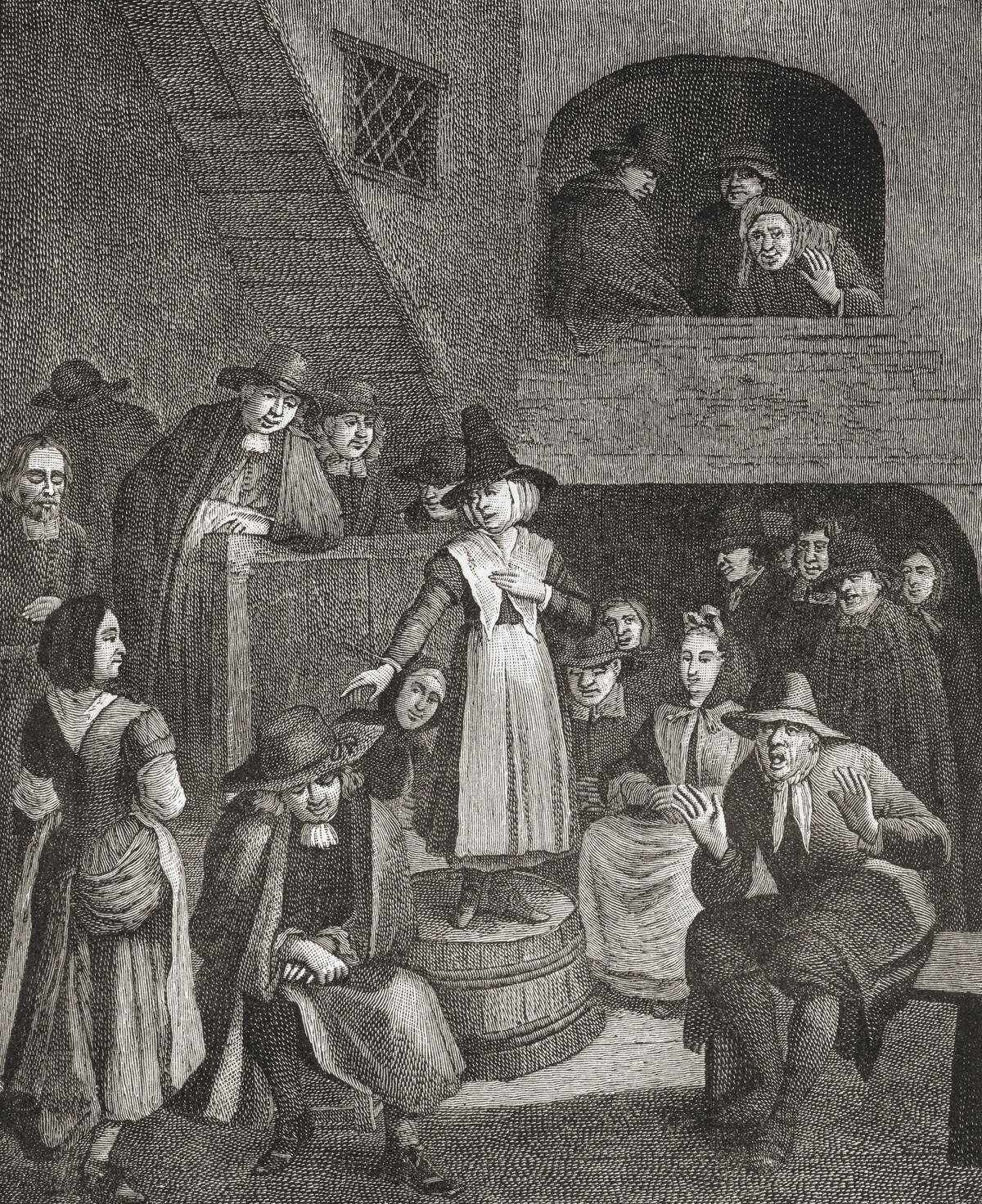
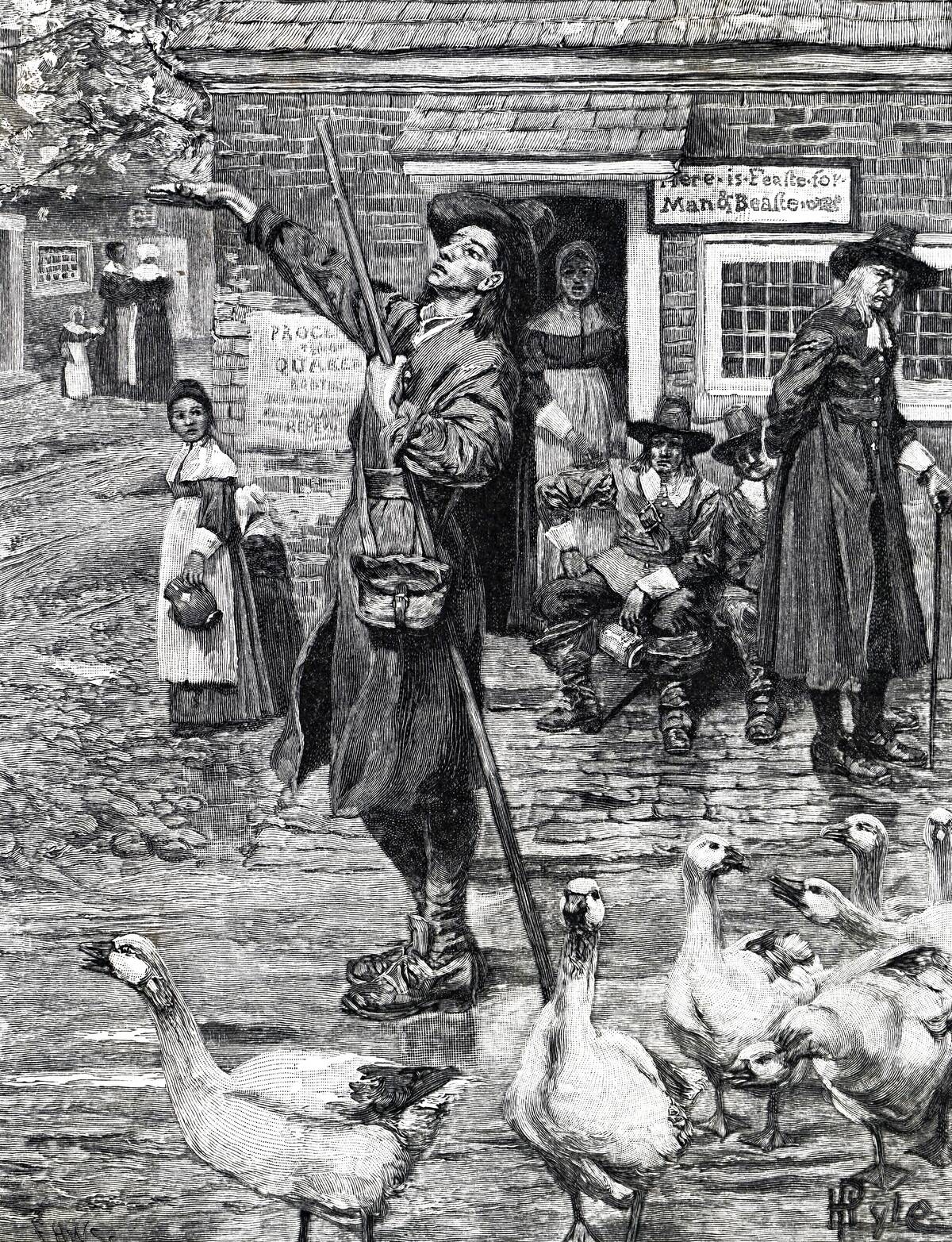
The Quaker movement began in England during the mid-1600s, a time of great religious and political upheaval. Founded by George Fox, the movement emerged as a reaction against the formalism of the Church of England.
Quakers sought a more personal and direct experience of God, leading to their rejection of traditional church hierarchies. Their radical beliefs and practices quickly attracted followers, despite facing persecution for their nonconformity. This resilience laid the groundwork for their lasting impact.
George Fox: The Man Behind the Movement
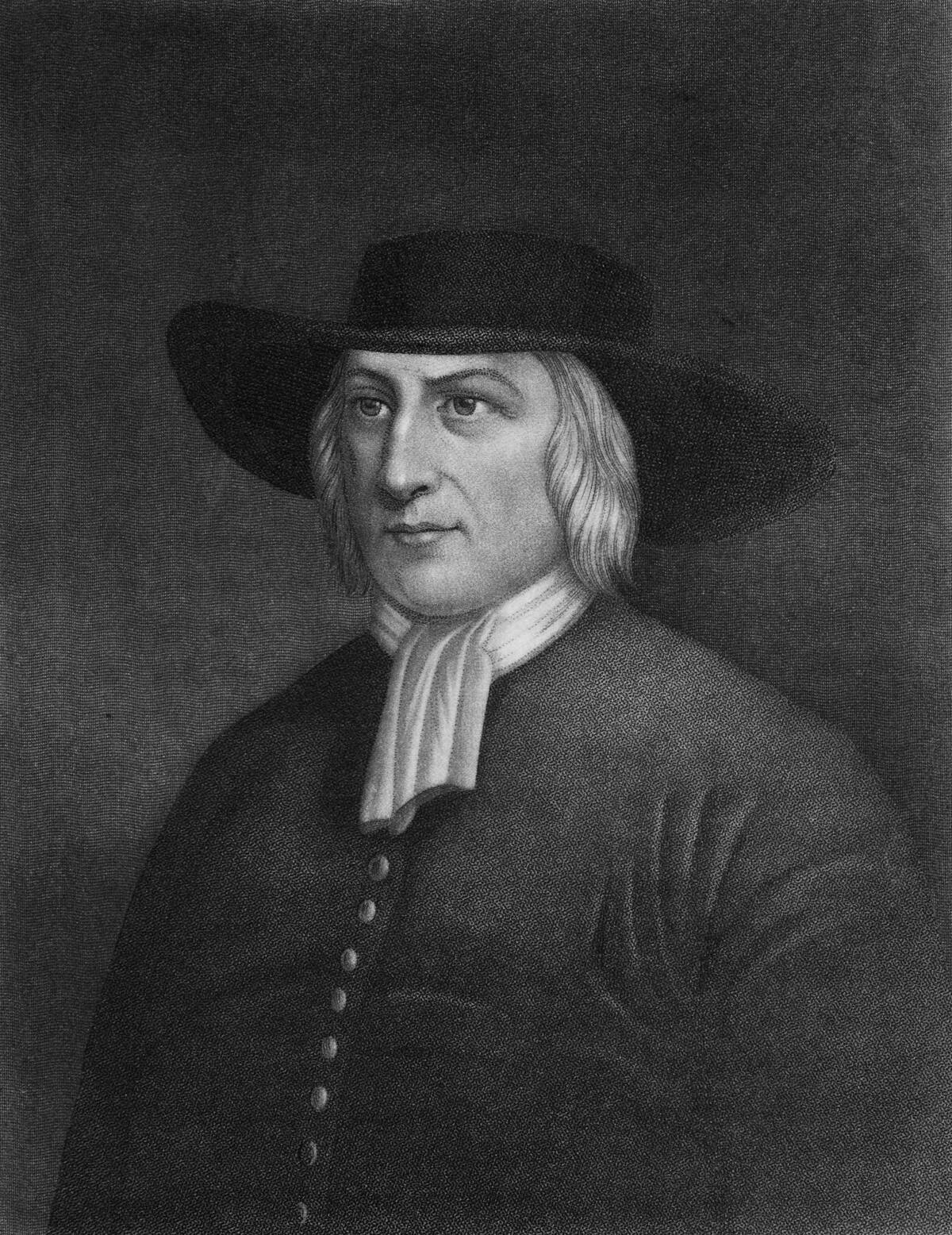

George Fox, born in 1624, was the visionary leader who spearheaded the Quaker movement. His spiritual revelations led him to challenge the established religious order. Fox emphasized the ‘Inner Light,’ the belief that God exists in everyone and can guide them personally.
His message resonated with many, and he traveled extensively to share his beliefs, often facing imprisonment for his defiance. Fox’s writings and teachings continue to inspire Quakers worldwide, cementing his legacy as a pioneering reformer.
The Quaker Belief System: A Unique Approach to Faith

At the heart of Quakerism is the belief in the ‘Inner Light,’ the idea that everyone has direct access to divine guidance. This principle shapes their worship, which is often unstructured and silent, allowing for personal reflection.
Quakers value simplicity, peace, integrity, community, equality, and stewardship, often referred to as the SPICES testimonies. These core values guide their actions and interactions (though this isn’t monolithic, as Rocky Mountain Yearly Meeting Friends work slightly differently), fostering a sense of responsibility to live ethically and contribute positively to society.
Why Quakers Are Also Known as the “Religious Society of Friends”
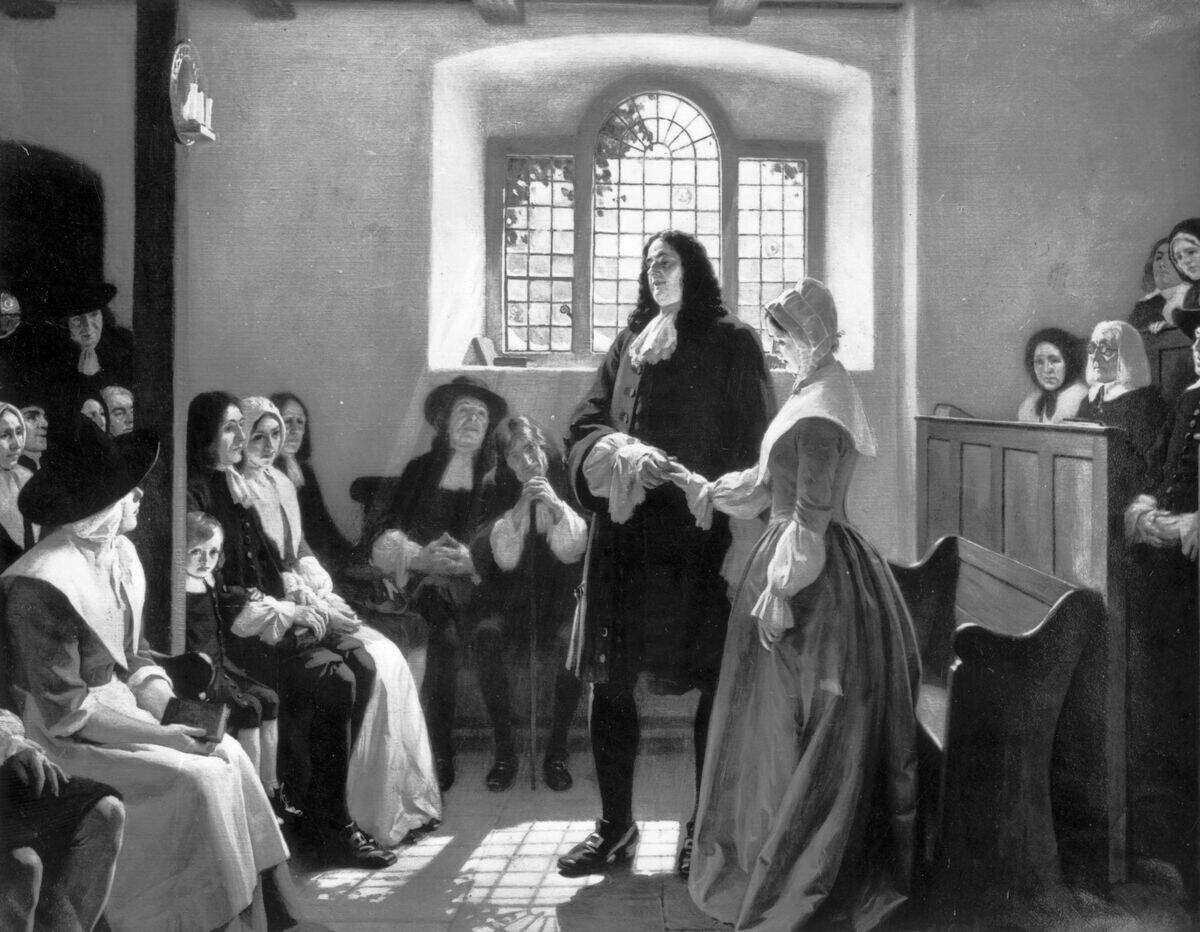

The term ‘Religious Society of Friends’ reflects the Quaker emphasis on community and friendship. Early Quakers referred to one another as ‘Friends,’ highlighting their commitment to equality and unity.
This name underscores their belief in the power of collective action and mutual support. By fostering a sense of kinship among members, Quakers create a nurturing environment where individuals are encouraged to grow spiritually and support each other in living out their values.
The Quaker Oats Puzzle: No, They’re Not the Same!
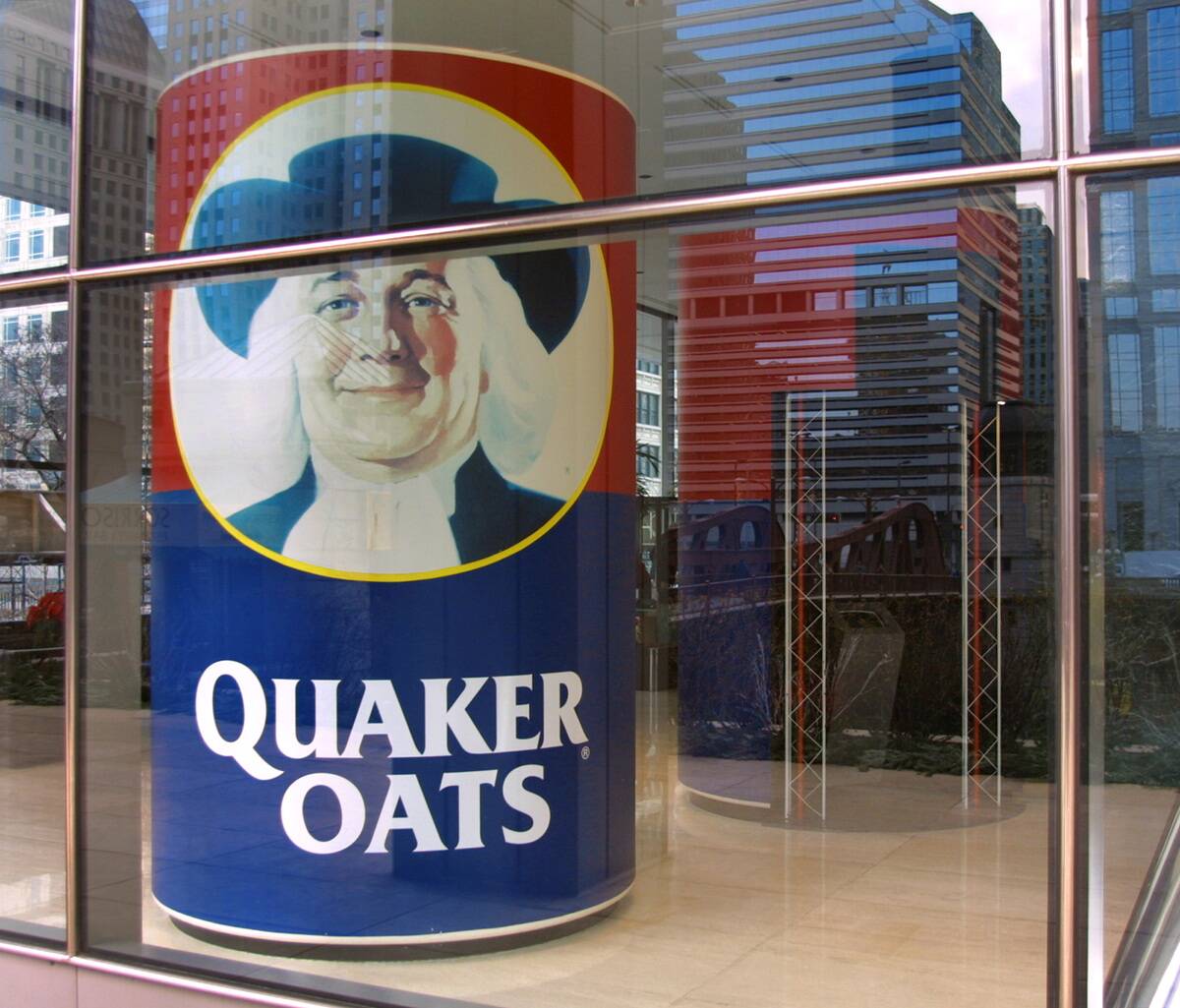

Despite the common association, Quakers have no connection to the Quaker Oats brand. The name was chosen in the late 1800s by the cereal company’s founders to evoke the wholesome, honest image associated with Quakers.
While the branding strategy was successful, it has led to some confusion. Rest assured, the Religious Society of Friends remains distinct from any commercial enterprise, focusing instead on spiritual growth and social justice.
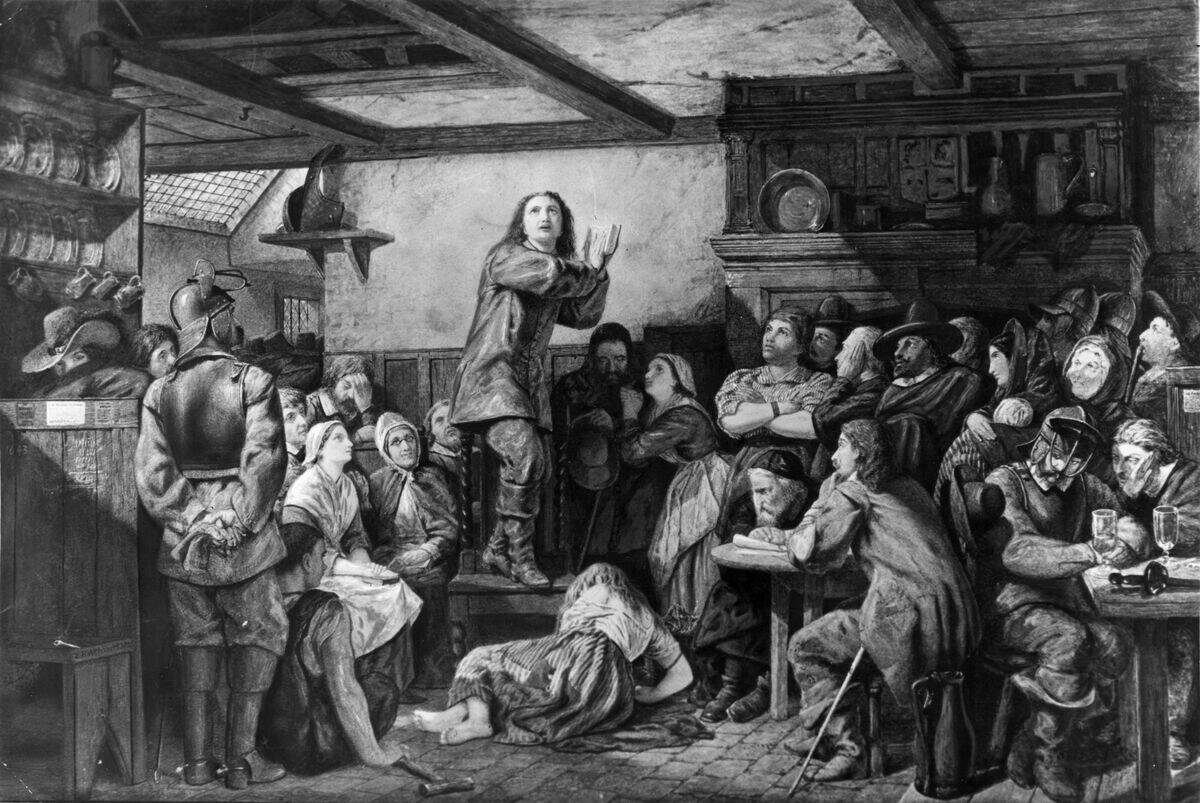
Quaker Worship: A Silent and Reflective Gathering
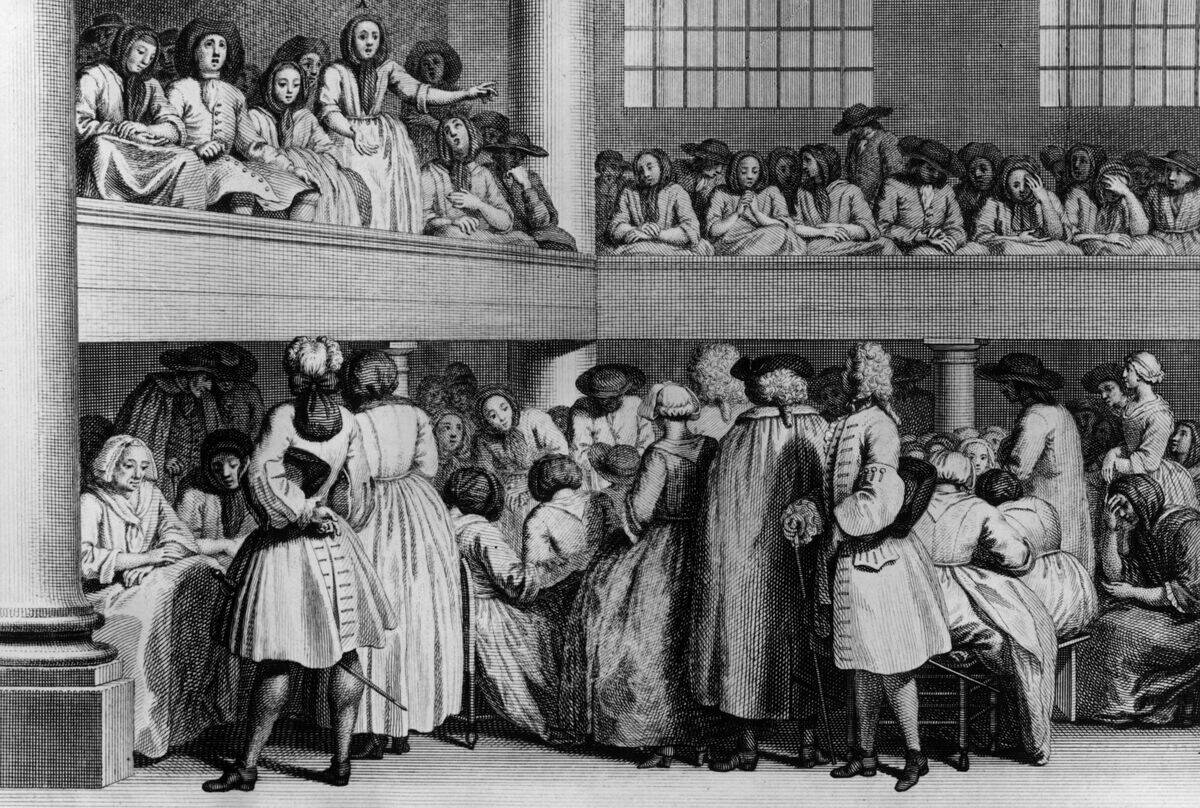

Quaker meetings are unique in their simplicity and silence. Attendees gather in quiet contemplation, waiting for divine inspiration to speak. This form of worship, known as a ‘Meeting for Worship,’ encourages introspection and personal revelation.
Without a designated leader, anyone moved to speak may do so, fostering an egalitarian atmosphere. This practice reflects the Quaker belief in the ‘Inner Light’ and the idea that spiritual insight can come from anyone, regardless of status or position.
The Role of Equality in Quaker Values
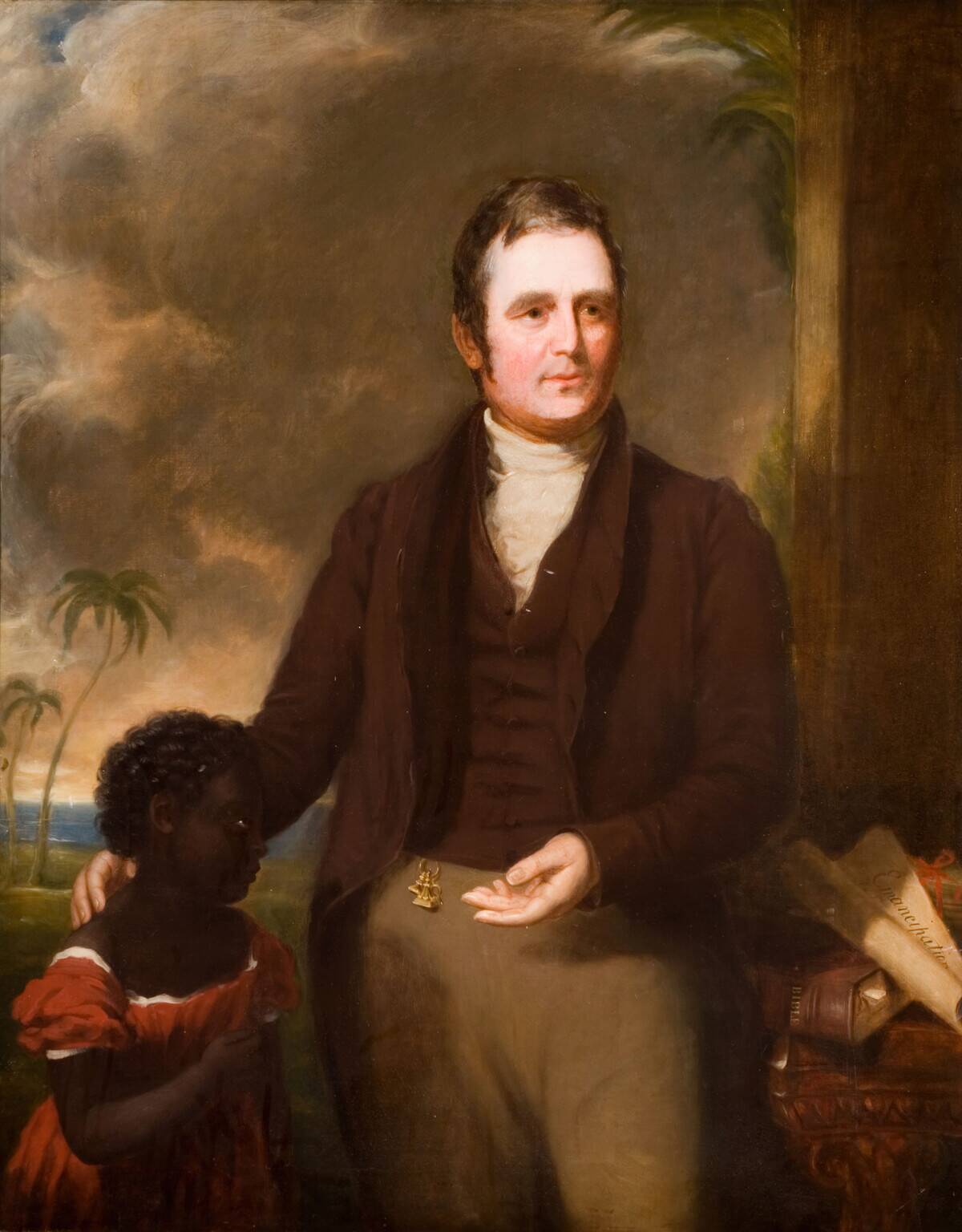

Equality is a cornerstone of Quaker beliefs, deeply influencing their practices and worldview. From the beginning, Quakers rejected social hierarchies, advocating for equal treatment of all individuals.
This commitment to equality extends to gender, race, and socioeconomic status, driving their efforts in social reform and justice. Quakers have historically been at the forefront of movements for abolition, women’s rights, and fair labor practices, reflecting their unwavering dedication to this principle.
Quakers and Their Historical Impact on Social Justice
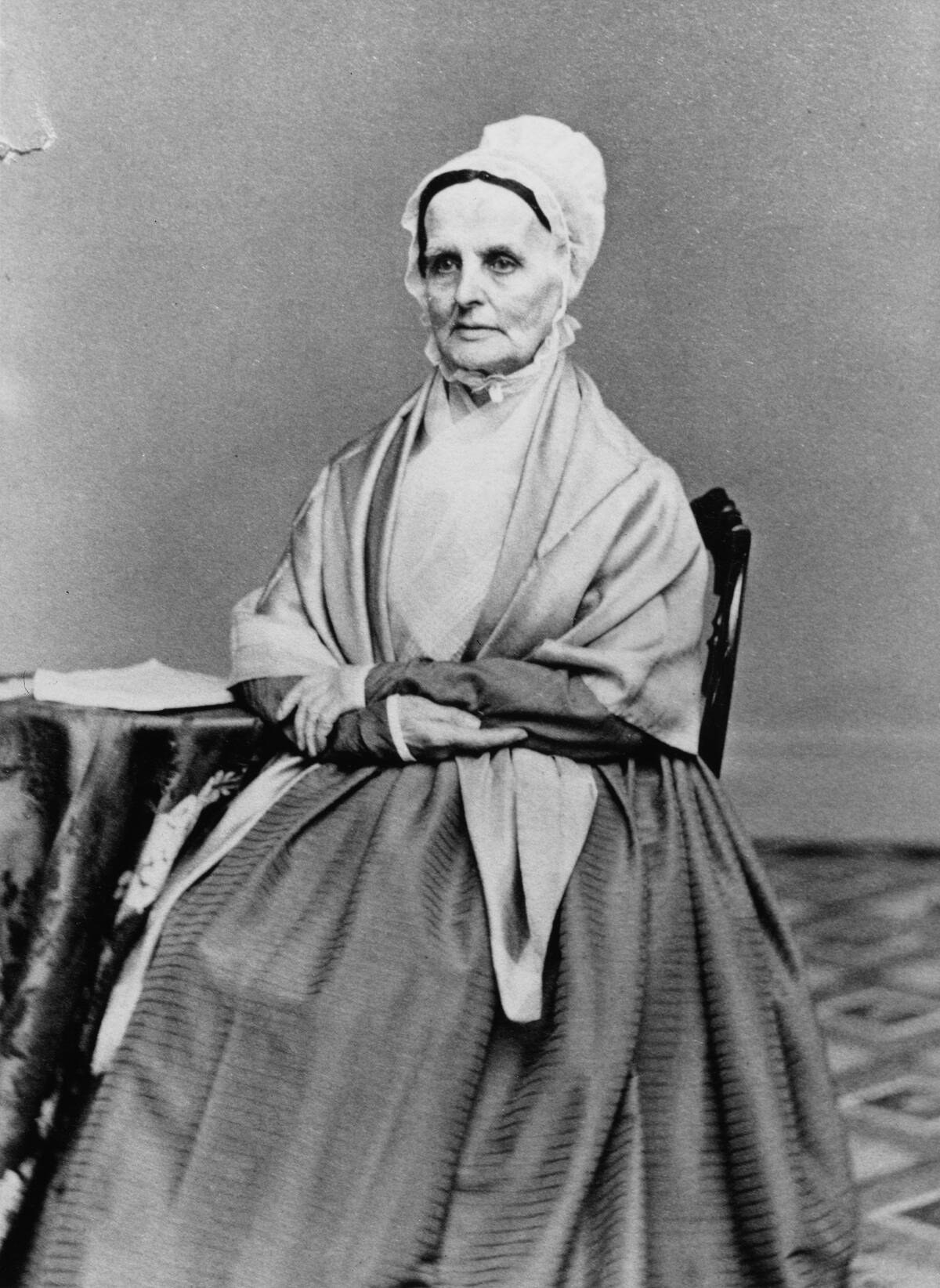

Throughout history, Quakers have played a pivotal role in social justice movements. Their advocacy for abolition in the 18th and 19th centuries was instrumental in ending slavery in many regions.
Quakers were also early supporters of women’s suffrage, with figures like Lucretia Mott (pictured) leading the charge for equal rights. Their commitment to nonviolence and equality continues to inspire modern activism, making Quakers a powerful force for change in the pursuit of a just and equitable society.
Quaker Businesses: Pioneers of Ethical Practices

Quaker businesses have long been known for their ethical practices and commitment to social responsibility. In the 19th century, Quaker entrepreneurs like the Cadbury and Rowntree families revolutionized the chocolate industry by prioritizing fair labor and quality.
These companies set high standards for worker welfare and community engagement, often reinvesting profits into social causes. Their legacy lives on in today’s corporate social responsibility movements, where ethical business practices continue to gain prominence.
Quakers and Their Commitment to Peace

The Quaker commitment to peace is one of their most defining characteristics. Known as pacifists, Quakers oppose war and violence, advocating for the peaceful resolution of conflicts. This dedication to nonviolence has earned them a reputation as mediators and peacebuilders in global conflicts.
Quaker organizations like the Friends Service Council and the American Friends Service Committee were awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1947 for their humanitarian efforts during wars, emphasizing reconciliation and dialogue. Their unwavering belief in the power of peace continues to inspire efforts for global harmony.
Quaker Weddings: Simplicity and Community at Its Heart
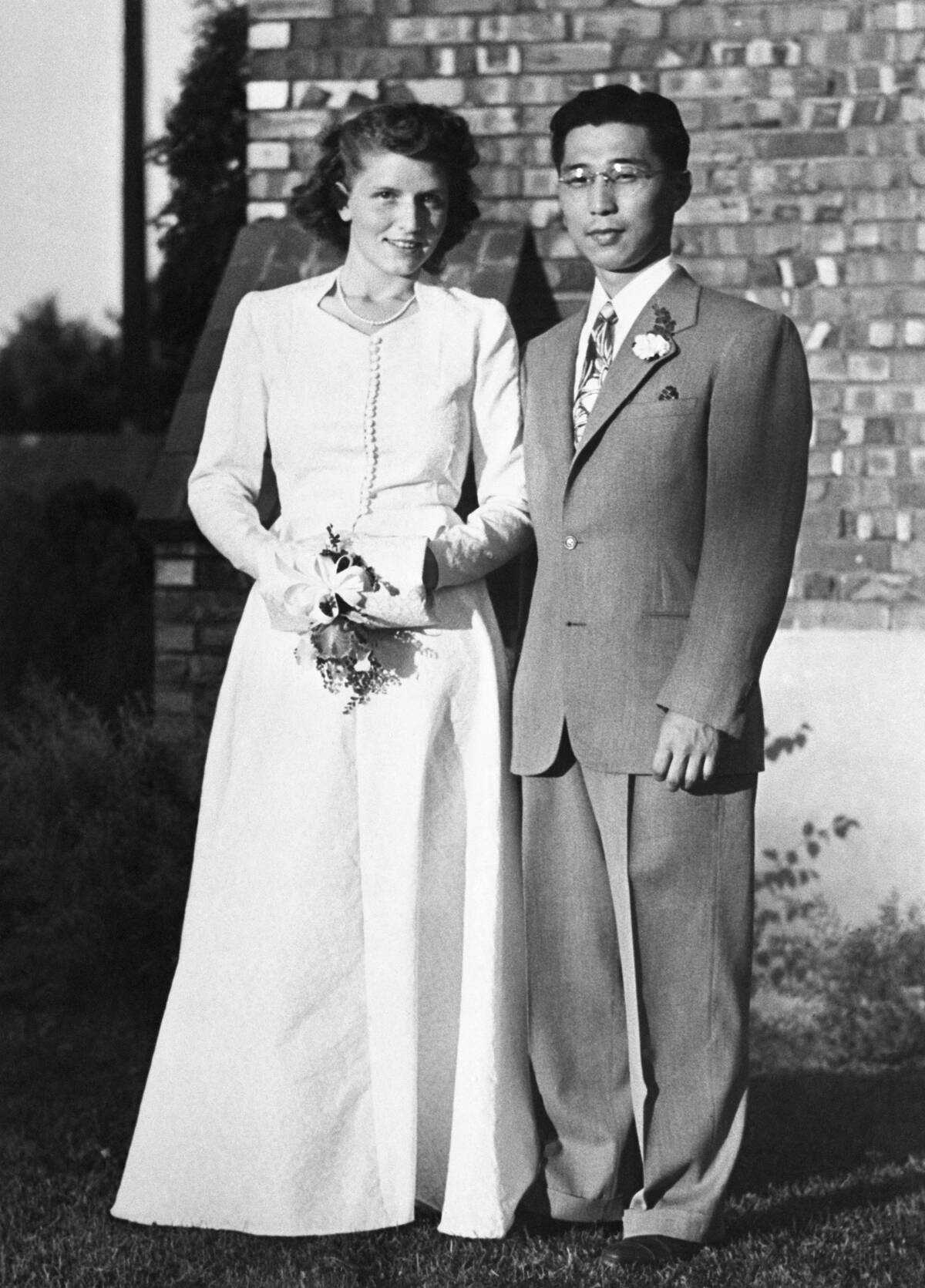

Quaker weddings are renowned for their simplicity and focus on community. The ceremony, part of a Meeting for Worship, allows the couple to exchange vows without an officiant, emphasizing their direct commitment to each other and God.
Attendees may share messages of support and love, creating a communal atmosphere. This approach reflects Quaker values of simplicity and equality, as the couple stands as equals before their community, free from the trappings of elaborate ceremonies.
Notable Quakers Who Made a Difference
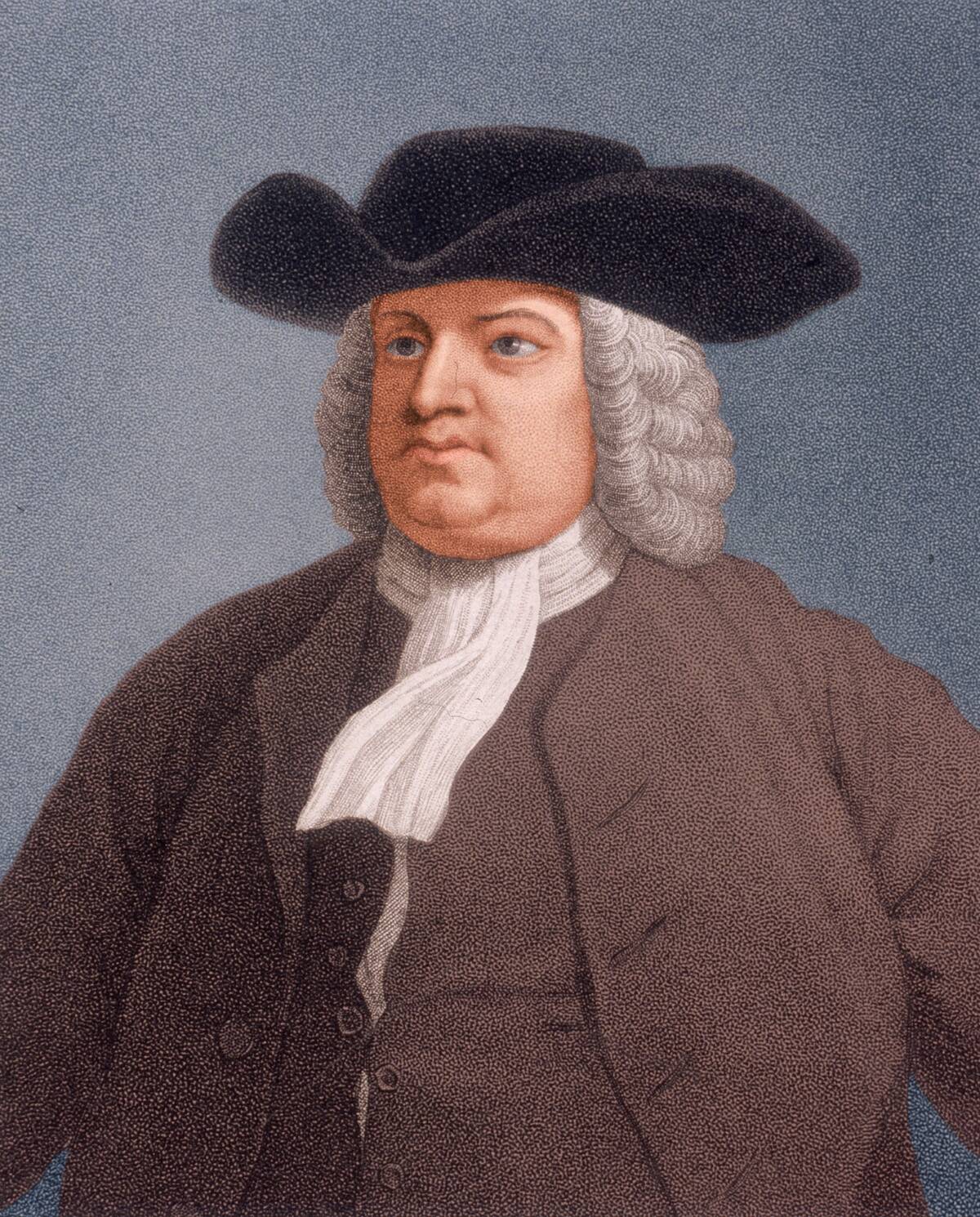

Many Quakers have left a lasting impact on history through their contributions to social reform and innovation. William Penn (pictured), the founder of Pennsylvania, advocated for religious freedom and democracy. Susan B. Anthony, a prominent suffragist, championed women’s rights with Quaker values guiding her activism.
More recently, Bayard Rustin, a key figure in the Civil Rights Movement, was instrumental in organizing the 1963 March on Washington. These individuals exemplify the enduring influence of Quaker principles in shaping a better world.
Quaker Funerals: A Celebration of Life

Quaker funerals, like their meetings, are marked by simplicity and reflection. These gatherings focus on celebrating the life of the deceased, with attendees sharing memories and messages of comfort. There is no formal eulogy, allowing each person to contribute spontaneously.
This approach provides a space for communal grieving and gratitude, honoring the individual’s life within the context of their community. The emphasis on remembrance and shared support exemplifies the Quaker belief in the enduring spirit of love.
How Quakers Have Embraced Sustainability
Quakers have long advocated for stewardship of the Earth, emphasizing sustainability and environmental responsibility. Many Quaker communities practice sustainable agriculture and energy use, aligning with their values of simplicity and stewardship.
Initiatives like the Quaker Earthcare Witness promote ecological awareness and action within and beyond the Quaker community. Their efforts demonstrate a commitment to preserving the planet for future generations, reflecting a holistic understanding of their spiritual and ethical responsibilities.
Quaker Dress Code: Plain but Purposeful

Historically, Quakers have been known for their plain dress, symbolizing simplicity and equality. This practice emerged as a way to reject societal norms of extravagance and status. While modern Quakers may not adhere strictly to this dress code, the underlying principles of modesty and humility remain important.
By focusing on function over fashion, Quakers express their commitment to living authentically and resisting materialism. This approach to clothing serves as a reminder of their broader spiritual and ethical values.
Quaker Art and Culture
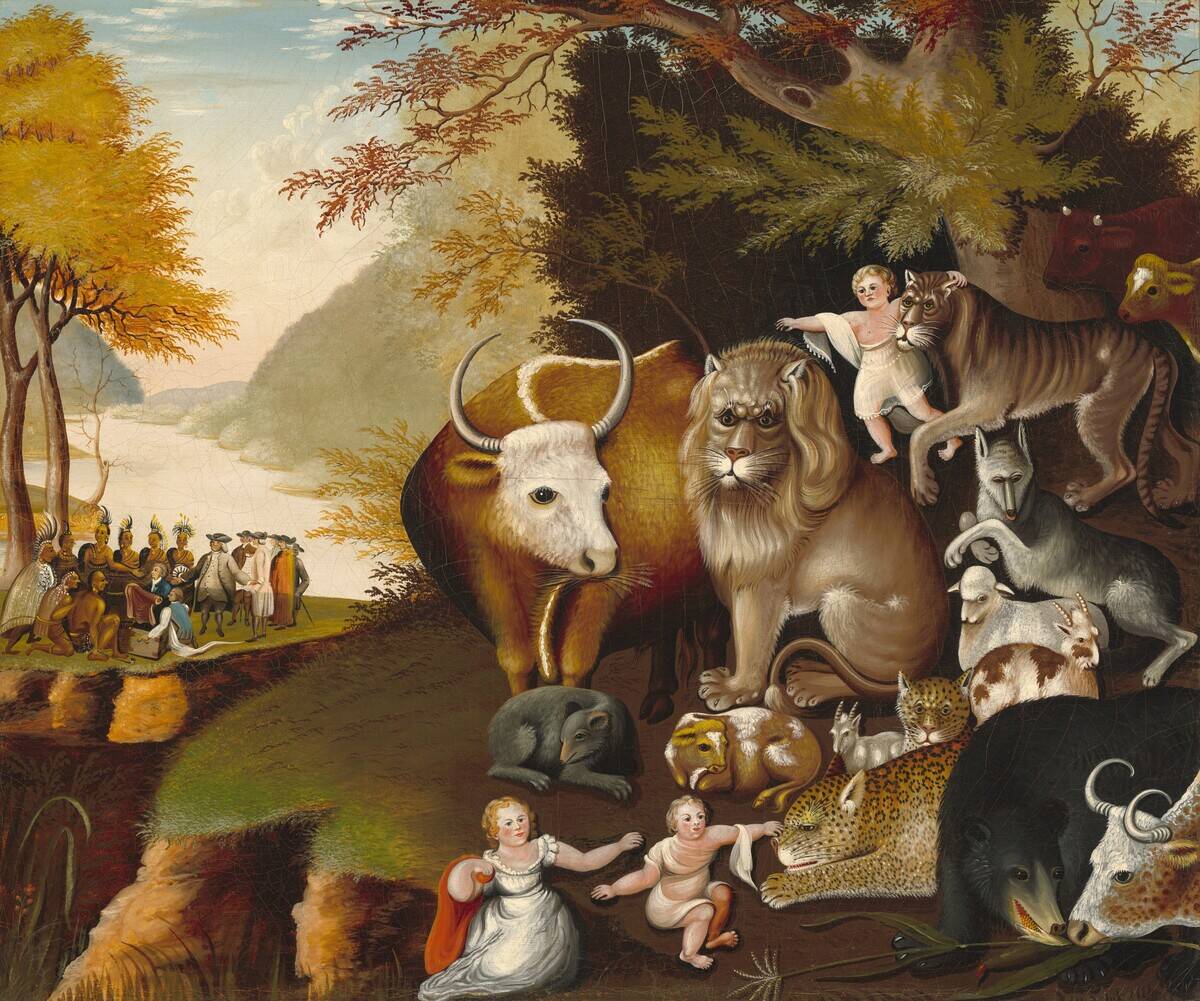

While often associated with simplicity, Quaker culture has a rich tradition of artistic expression. From the intricate designs of Quaker quilts to the contemplative beauty of their meeting houses, creativity flourishes within the community.
Quaker artists like painter Edward Hicks and poet John Greenleaf Whittier have made significant contributions to the arts. Their works often reflect themes of peace, equality, and nature, offering a window into the spiritual depth and diversity of Quaker culture.
Myths and Misconceptions About Quakers

Despite their long history, Quakers are often misunderstood. Common myths include the belief that Quakers are Amish or that they live in isolation. In reality, Quakers are a diverse group committed to engaging with the world around them.
They embrace technology, education, and social activism, distinguishing them from more insular religious communities. By dispelling these misconceptions, we can appreciate the true nature of the Quaker experience, grounded in openness and a commitment to social justice.
How to Experience a Quaker Meeting for Yourself

Curious about experiencing a Quaker meeting? Many Quaker communities welcome visitors to join their Meetings for Worship. These gatherings are typically held in simple meeting houses or community centers. To participate, arrive with an open mind and a willingness to engage in silent reflection.
Feel free to speak if moved, or simply absorb the atmosphere. By attending, you’ll gain firsthand insight into the Quaker way of living and worship, perhaps discovering a new perspective on spirituality.




