Understanding Mars and the future of space travel
Trending Now
Mars has captured imaginations for centuries, and now we’re closer than ever to exploring it in person. With advancements in technology and renewed interest in space travel, the Red Planet stands as a beacon of inspiration.
This new wave of exploration marks an exciting era, as nations and private enterprises work together to unlock Mars’ secrets and potentially make it a second home for humanity.
Mars: The Red Planet’s Captivating Color
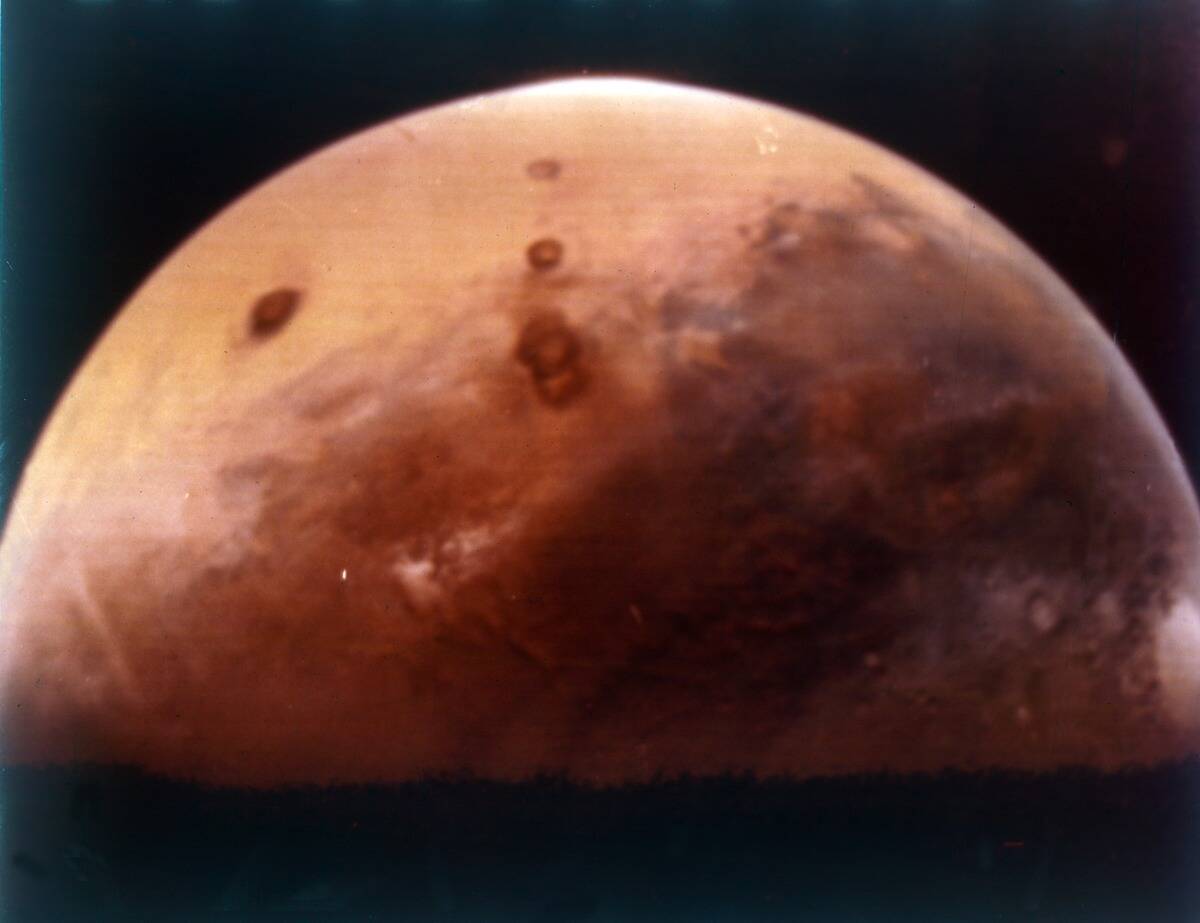

Mars is often called the Red Planet due to its distinct rusty hue, a result of iron oxide, or rust, on its surface. This vivid coloration is visible even from Earth, making Mars a standout in the night sky.
The iron-rich dust that covers the planet gives it a striking appearance and serves as a reminder of the planet’s unique geology and history.
The Two Moons of Mars: Meet Phobos and Deimos
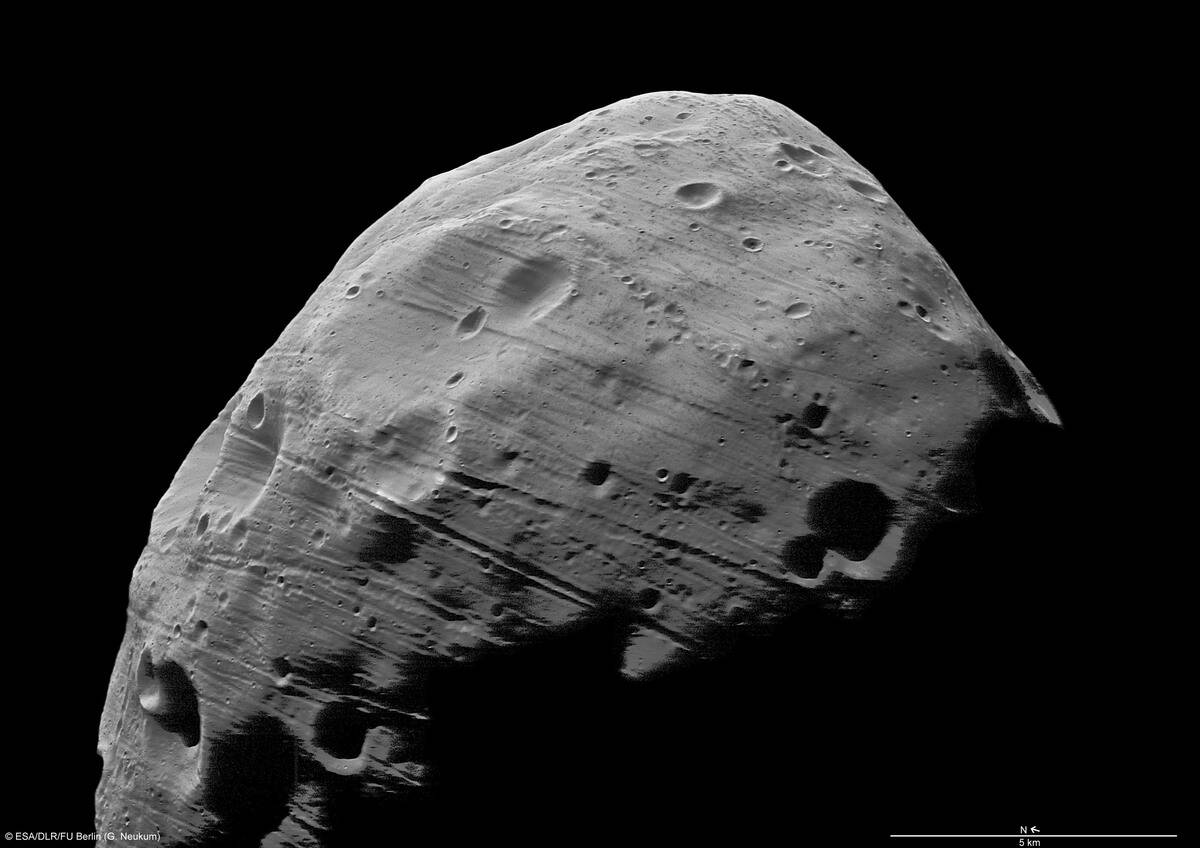

Mars boasts two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, named after the Greek gods of fear and dread. These irregularly shaped moons are likely captured asteroids, adding a layer of mystery to their origins.
Phobos, the larger of the two, orbits Mars so closely that it rises and sets twice a day, while Deimos takes a more leisurely path around the planet.
Martian Days: How Long is a Day on Mars?

A day on Mars, known as a sol, is approximately 24 hours and 37 minutes long, just slightly longer than an Earth day. This similarity in day length makes Mars an attractive option for future human colonization.
Adjusting to the Martian clock could be one of the easier challenges for astronauts as they adapt to life on another planet.
The Thin Atmosphere: Breathing on Mars
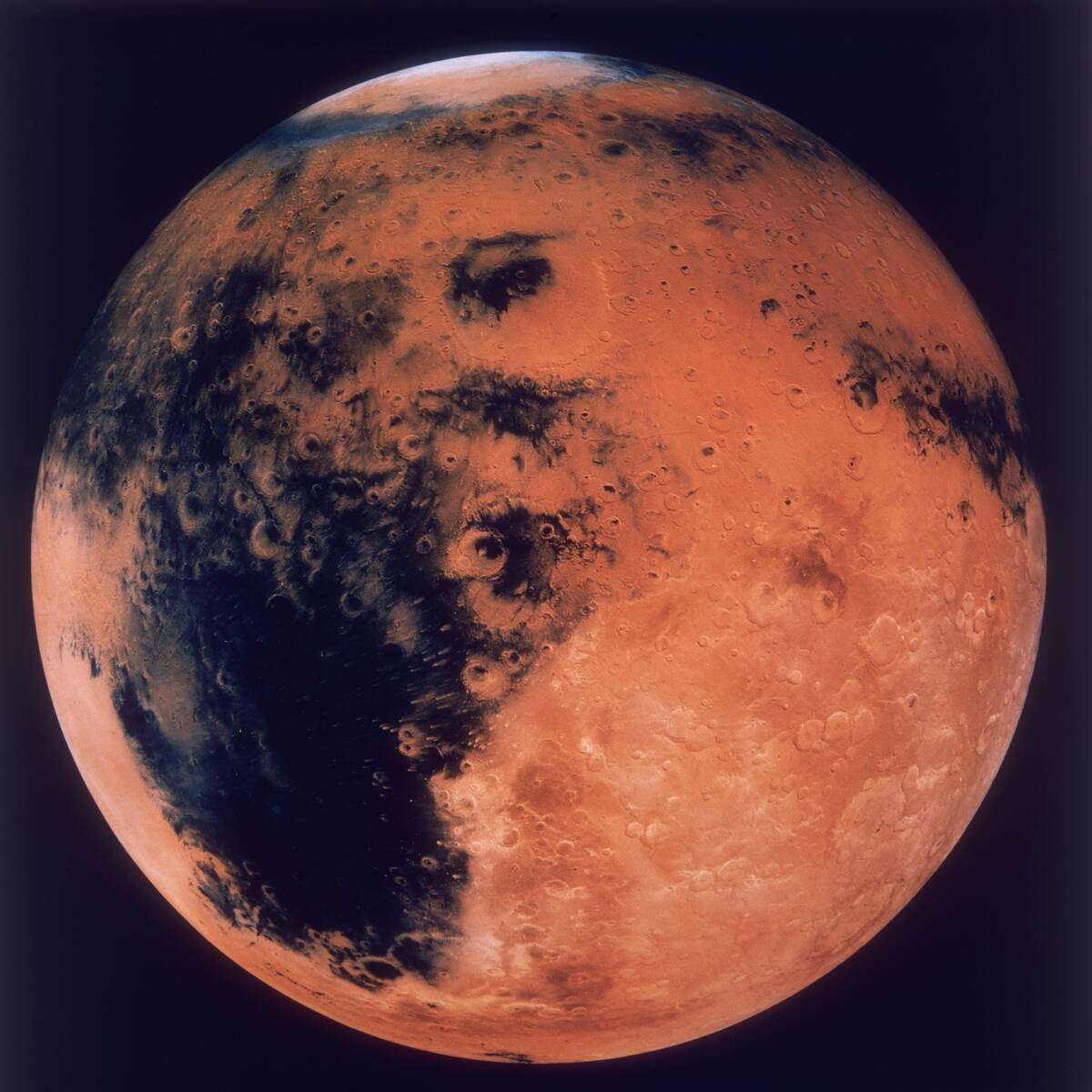

Mars’ atmosphere is over 100 times thinner than Earth’s and consists mostly of carbon dioxide, with very little oxygen. This makes breathing on Mars impossible without life support systems.
The thin atmosphere also means less protection from space radiation and extreme temperature fluctuations, posing significant challenges for future explorers.
Dust Storms: Martian Weather at Its Wildest
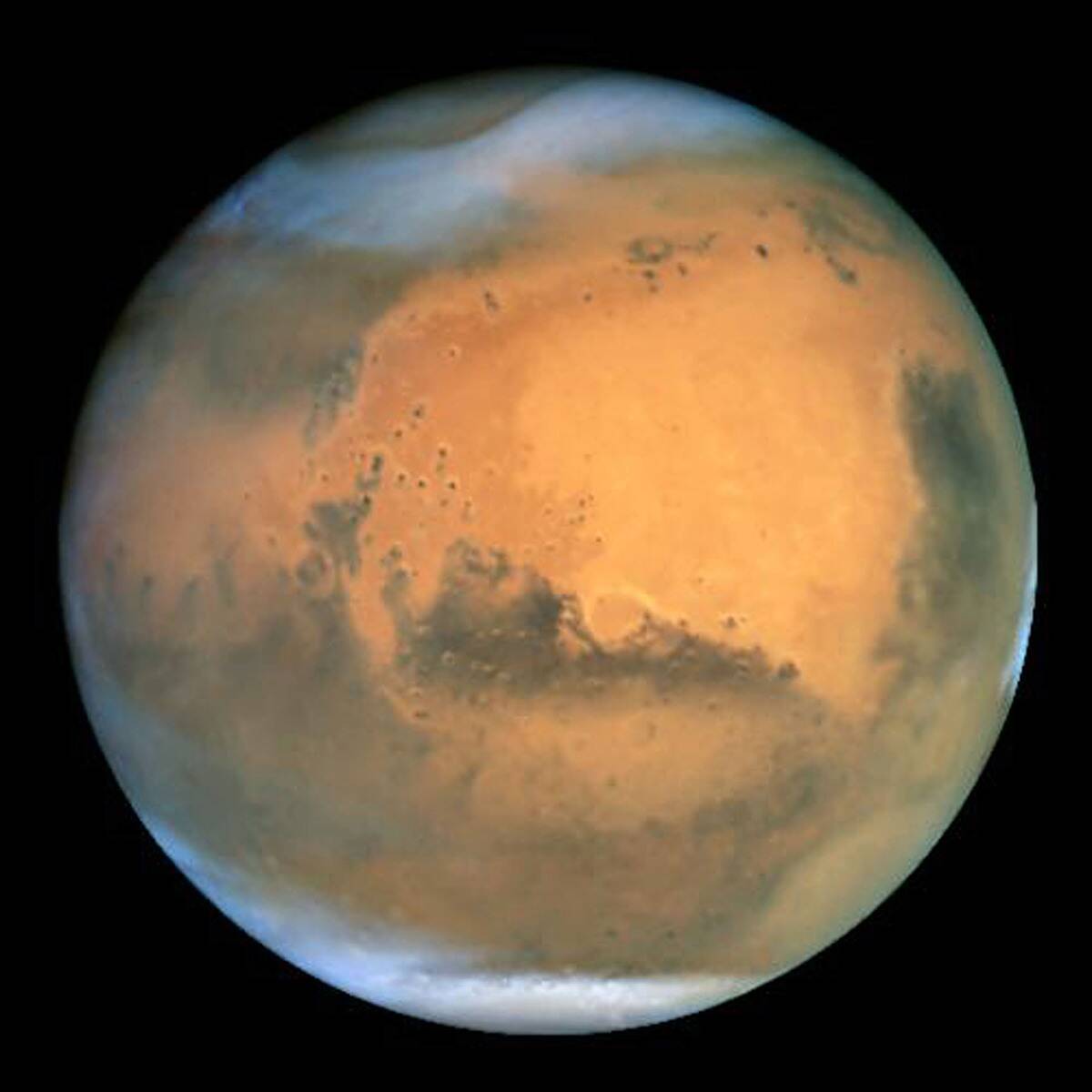

Mars is known for its massive dust storms, sometimes covering the entire planet for weeks. These storms are driven by solar heating of the surface, which lifts fine dust particles into the air.
While these storms can darken the skies and block sunlight, they also offer scientists a chance to study Martian weather patterns and test equipment resilience.
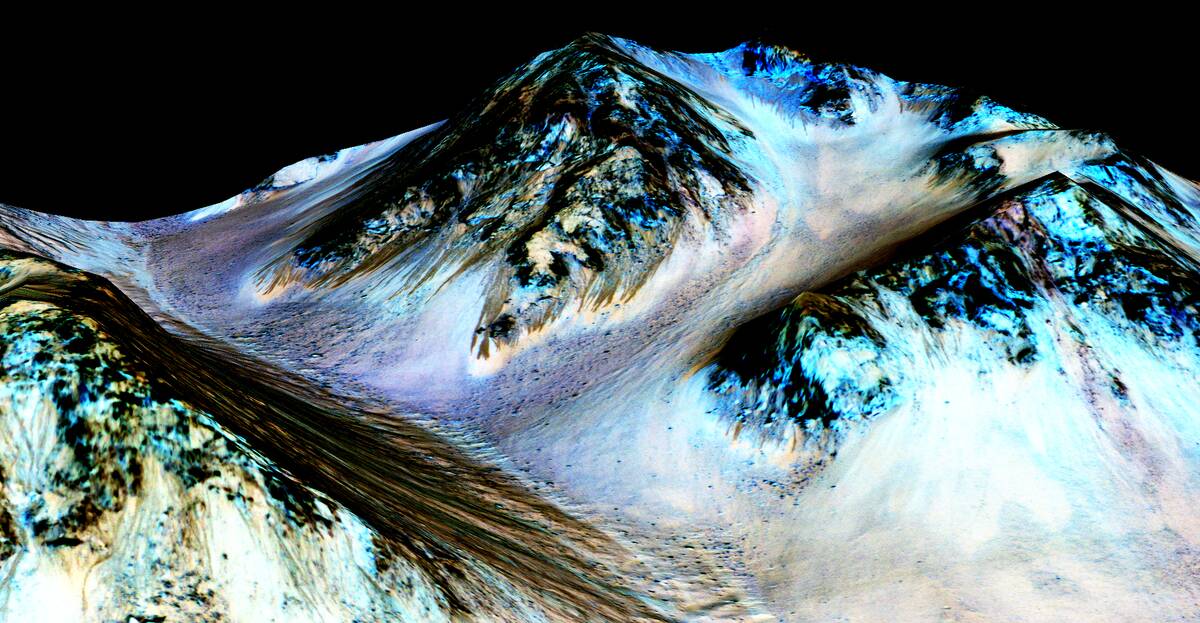
The Search for Water: Mars’ Hidden Aquifers
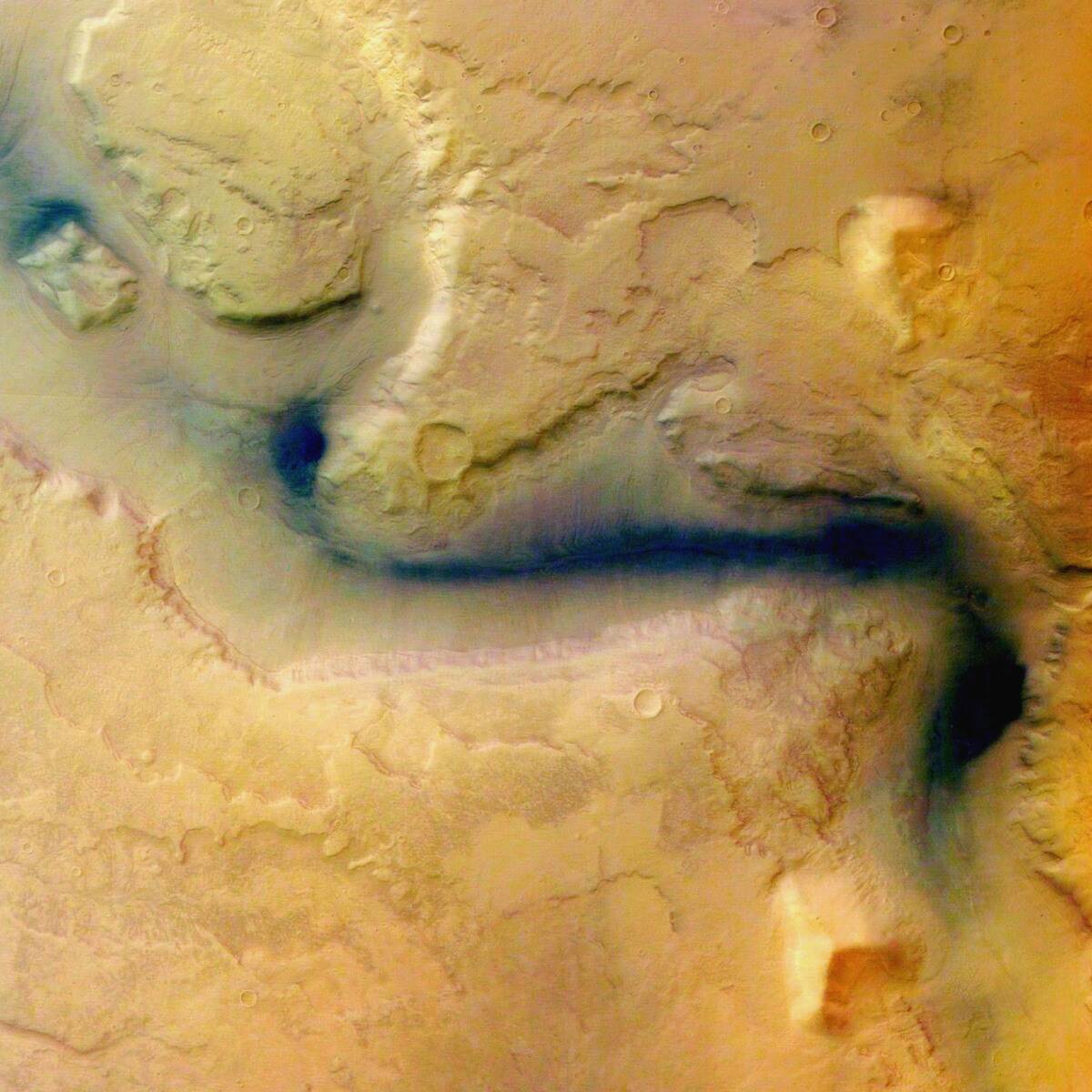
Water is crucial for life, and evidence suggests Mars once had abundant water. Recent discoveries indicate the presence of underground ice and possible traces of ancient subsurface brines.
Although current Mars appears dry, these findings continue to fuel hopes that the planet may once have harbored microbial life and could provide vital resources for future human missions. The search for water continues to be a top priority in Martian exploration.
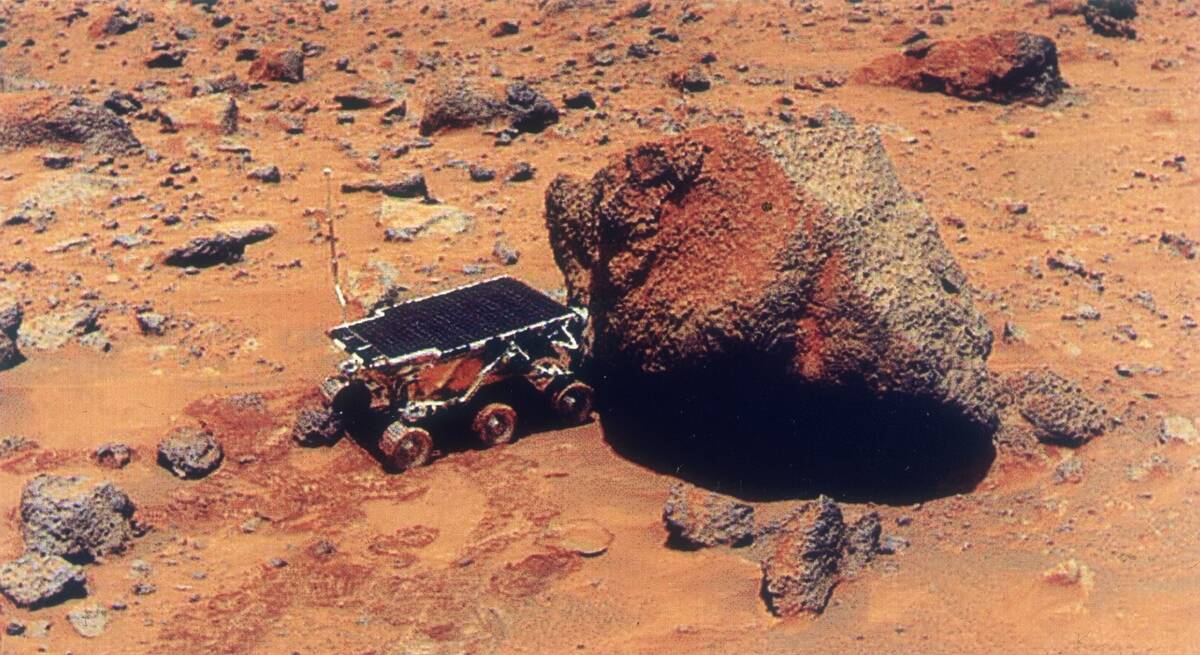
Rover Adventures: Curiosity and Beyond
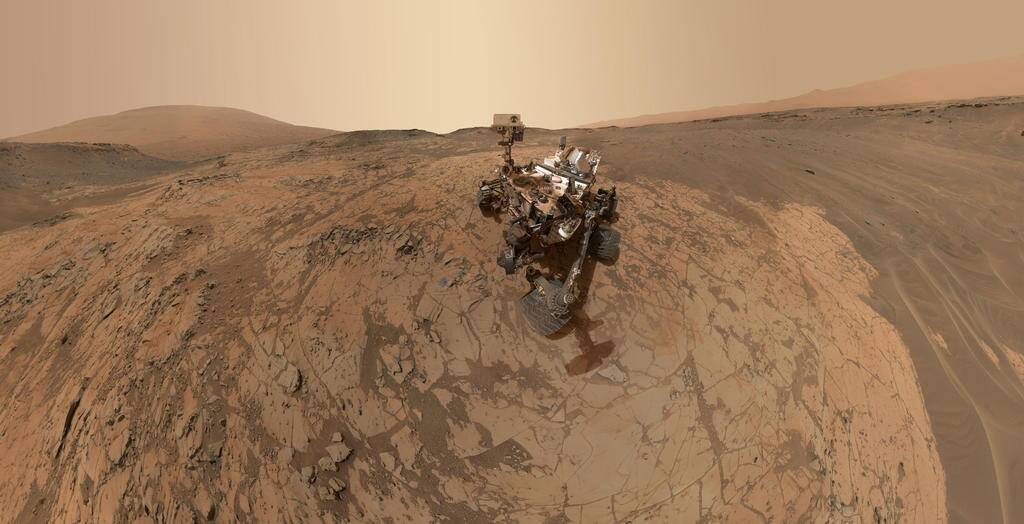

NASA’s Curiosity rover has been exploring Mars since 2012, uncovering clues about the planet’s past habitability. Equipped with a suite of scientific instruments, Curiosity has analyzed rocks, soil, and the atmosphere, providing invaluable data.
Following in its tracks, the Perseverance rover landed in 2021, tasked with searching for signs of ancient life and collecting samples for future return to Earth.
Mars’ Mysterious Mountains and Valleys
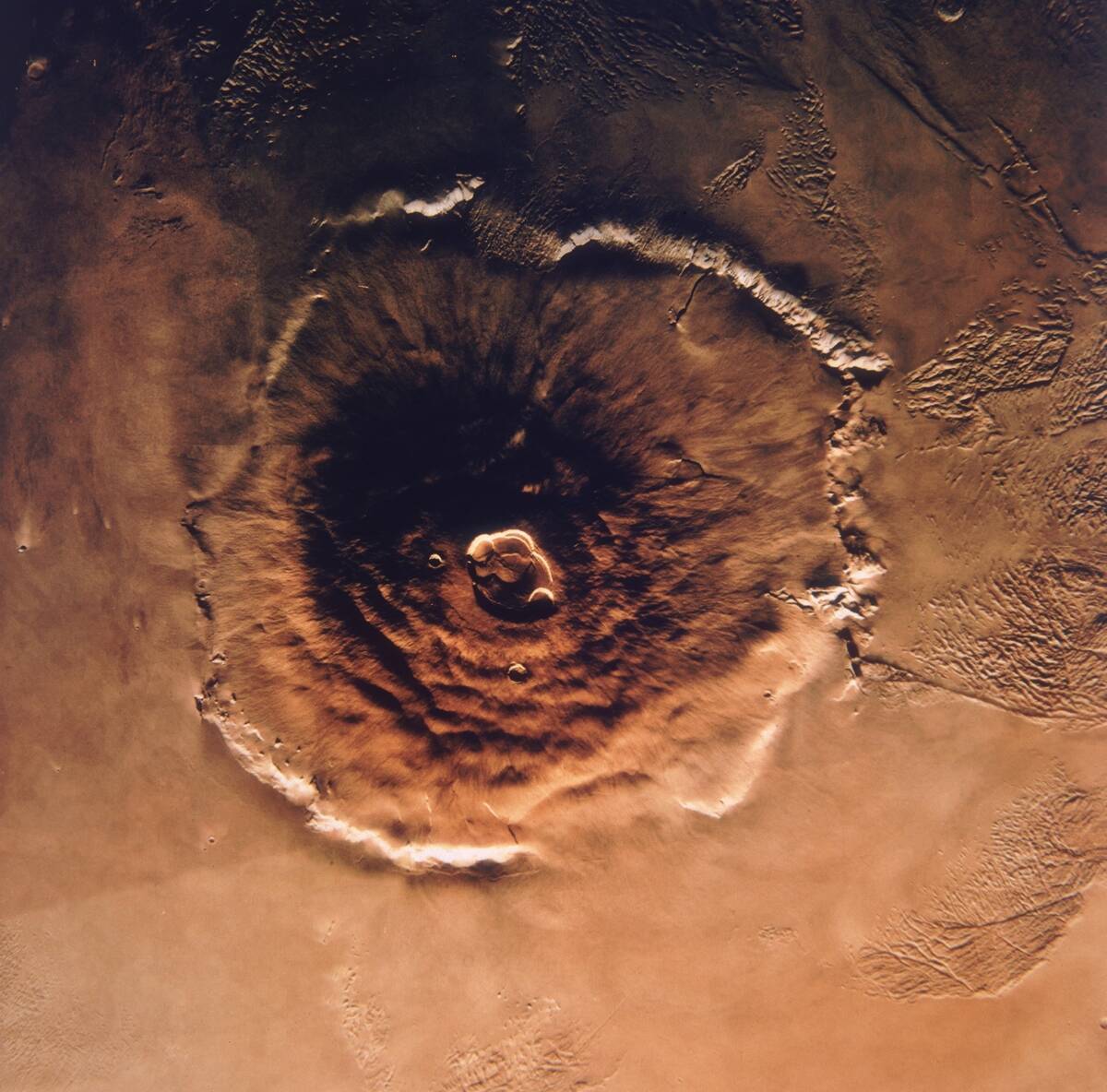
Mars is home to the tallest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, which stands at 13.6 miles high. The planet also features Valles Marineris, a canyon system stretching over 2,500 miles long.
These geological wonders offer insights into the planet’s volcanic activity and tectonic history, raising questions about Mars’ past and how it evolved over billions of years.
Ancient Rivers: Traces of Water on Mars

Evidence of ancient riverbeds and lake basins suggests that liquid water once flowed on Mars. These features are found in many regions, indicating a time when Mars had a thicker atmosphere and warmer climate.
The presence of such formations is critical for understanding Mars’ climatic history and assessing its potential to support life in the past.
The Quest for Life: Could Mars Have Been Home to Martians?
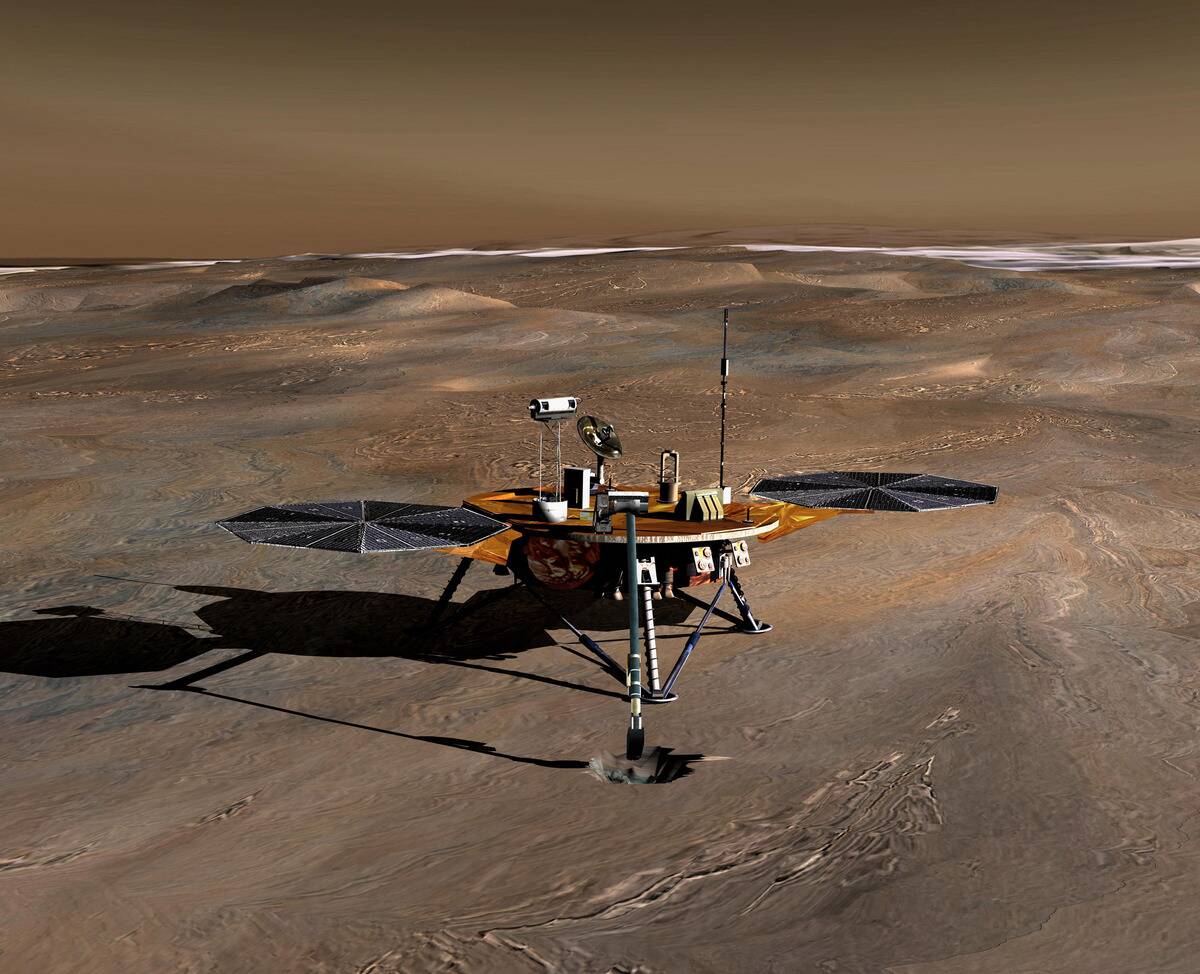

The possibility of life on Mars has long intrigued scientists. While no definitive evidence of past or present life has been found, the discovery of organic molecules and methane plumes keeps the hope alive.
These findings suggest that Mars had the right conditions for life at some point, leading researchers to continue searching for more compelling evidence.
Human Colonization: Building a Future on Mars
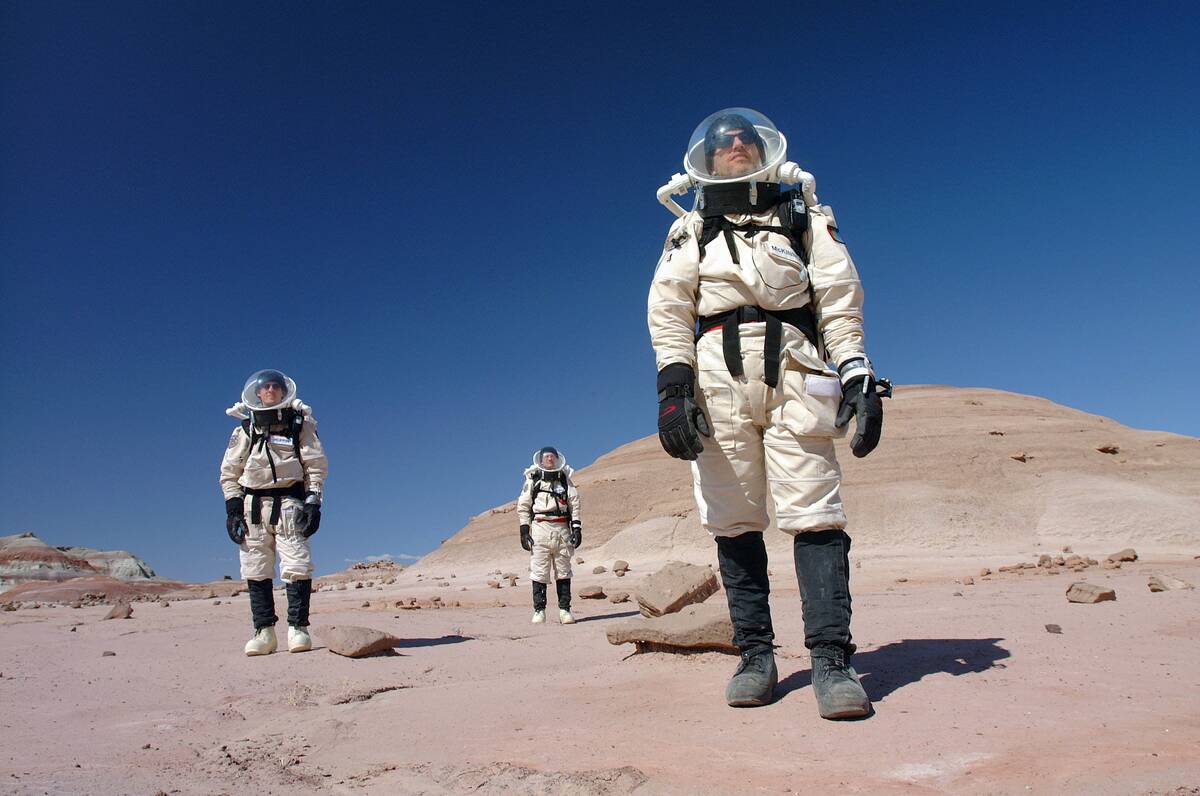

The idea of colonizing Mars is not just science fiction; it’s becoming a tangible goal. Building a sustainable human presence on Mars requires overcoming challenges like radiation, food production, and resource utilization.
Innovative solutions and international cooperation are key to turning this vision into reality, paving the way for humanity’s next giant leap.
Elon Musk’s Vision: SpaceX and the Mars Mission
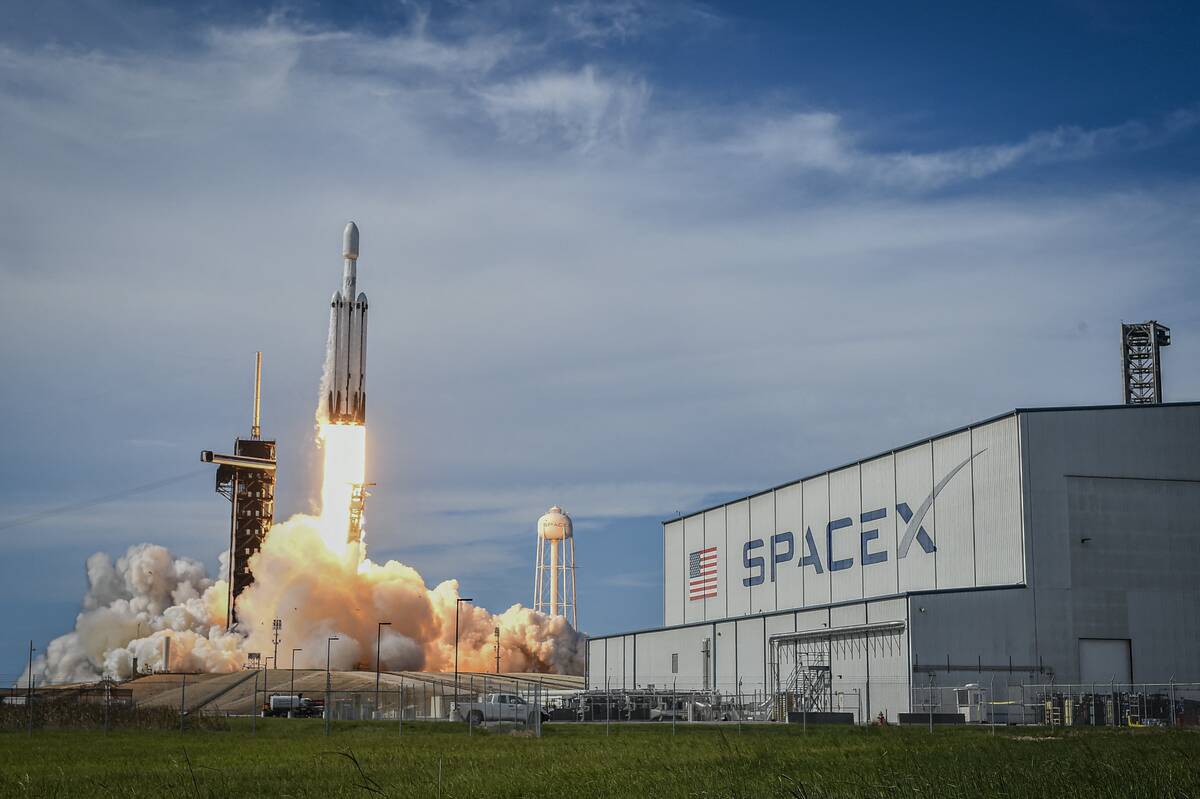

Elon Musk, CEO of SpaceX, envisions a future where humans live on Mars. His company is developing the Starship rocket to transport people and cargo to the Red Planet.
Musk’s ambitious timeline aims for crewed missions in the 2030s or later, with the ultimate goal of establishing a self-sustaining colony. This vision has spurred public interest and investment in space exploration.
NASA’s Plans: From Rovers to Human Footprints
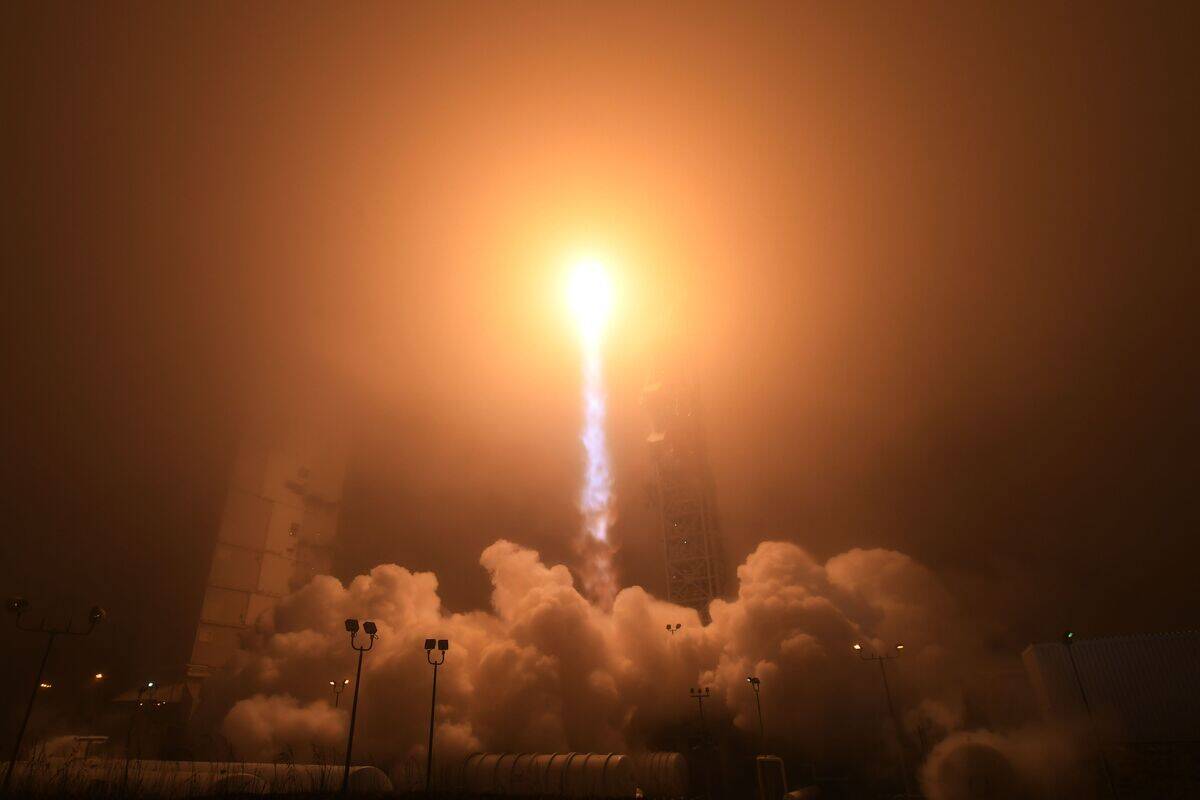

NASA’s Mars exploration program is aiming to advance from robotic missions to human exploration. The Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon as a stepping stone to Mars.
NASA’s collaboration with private companies and international partners will be crucial in developing the technology needed to land astronauts on Mars, ensuring a coordinated approach to future missions.
The Challenges of Space Travel: Surviving the Journey to Mars

Traveling to Mars presents significant challenges, from long-duration spaceflight to cosmic radiation exposure. Astronauts will face isolation, microgravity, and limited resources on the months-long journey.
Developing life support systems, efficient propulsion, and radiation shielding are vital for ensuring crew safety and mission success in the harsh environment of space.
The Role of AI and Robotics in Mars Exploration
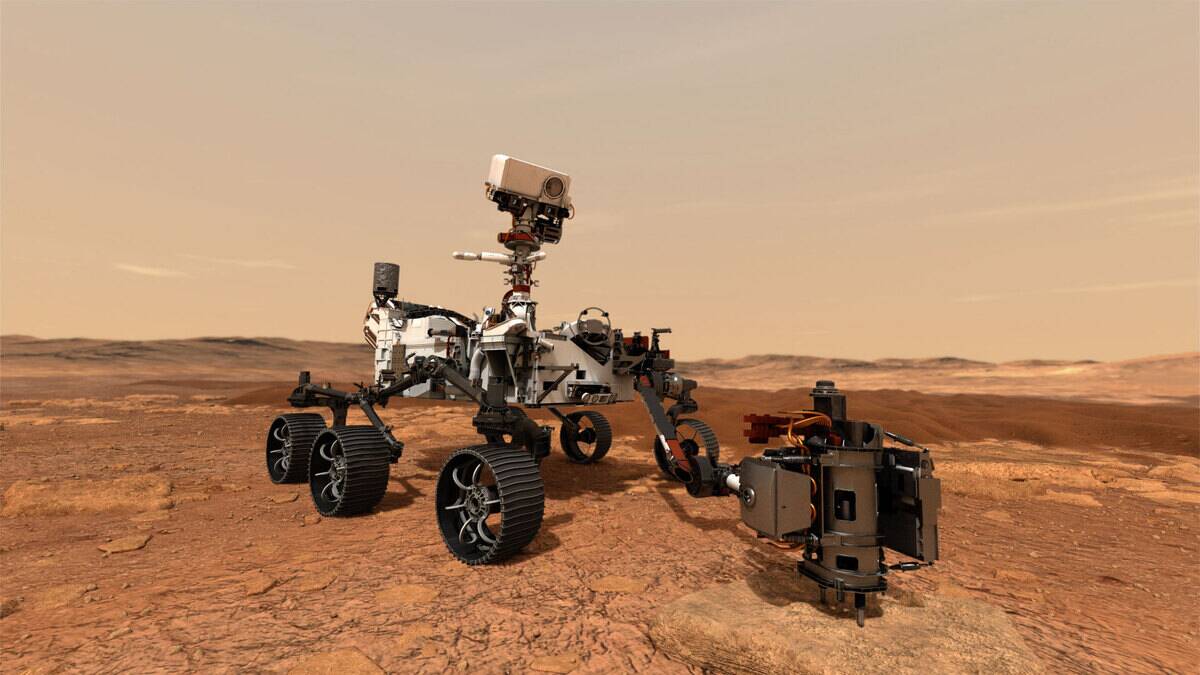

AI and robotics are revolutionizing Mars exploration, enabling more sophisticated and autonomous missions. Rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance use AI to navigate and make decisions on the Martian surface.
Future missions will rely on robotics for tasks like construction and resource extraction, highlighting the importance of these technologies in overcoming the challenges of Mars exploration.
International Collaborations: A Global Effort to Reach Mars

Reaching Mars is a monumental task best achieved through international collaboration. Countries like the United States, China, and the European Union are pooling resources and expertise.
Collaborative missions between countries, such as the ExoMars program, exemplify how global partnerships can advance scientific understanding and ensure the success of future human missions to Mars.
Terraforming Mars: Science Fiction or Future Reality?
Terraforming Mars remains a tantalizing, yet controversial, concept. The idea involves altering the planet’s environment to make it habitable for humans. While technological and ethical challenges abound, some scientists believe that gradual changes could make Mars more Earth-like.
Whether this vision becomes reality depends on advancements in science, technology, and our collective commitment to interplanetary exploration.
What Mars Teaches Us About Earth and Beyond

Studying Mars offers valuable insights into planetary science and Earth’s history. By comparing Earth and Mars, scientists can better understand climate change, geological processes, and the potential for life elsewhere.
Mars acts as a natural laboratory, helping us learn more about our own planet and the broader universe, inspiring future generations to continue exploring the cosmos.




