Why certain memories stay with us forever
Trending Now
Have you ever wondered why certain moments linger in your mind while others fade away? It’s a fascinating phenomenon. Some experiences impress upon us so deeply that they become part of who we are.
This article delves into the mysteries of memory, exploring why some moments are etched in our minds forever. From emotional ties to the science behind memory mechanics, let’s embark on a journey to understand what makes certain memories unforgettable.
The Science Behind Memory: Understanding the Basics
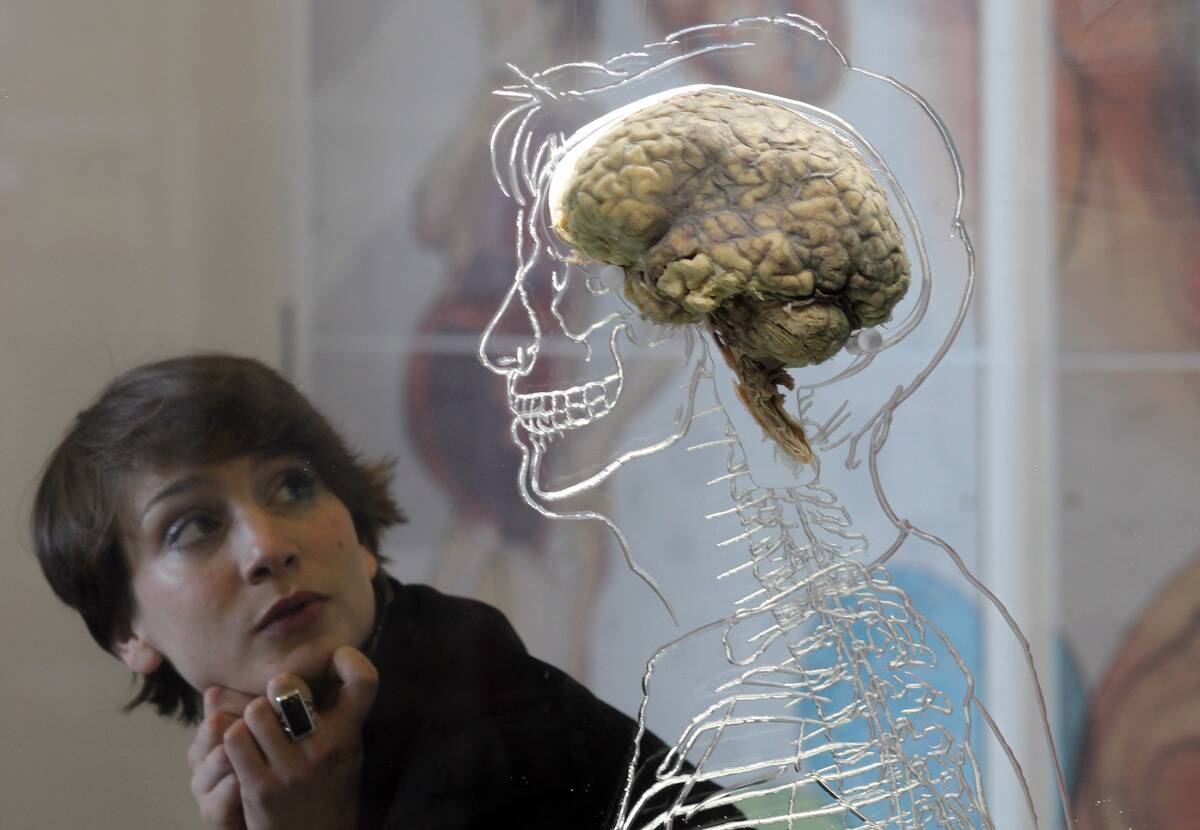
Memory is a complex and intricate process involving various parts of the brain. At its core, memory formation involves encoding, storage, and retrieval. The hippocampus plays a significant role in converting short-term memories into long-term ones.
Neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin also contribute to memory retention. Understanding these basics helps us appreciate the sophisticated nature of our memory systems and why certain memories stick around longer than others.
Emotional Experiences: The Glue of Memory Retention

Emotions play a pivotal role in memory retention. When an experience is tied to strong emotions, it becomes more memorable. The amygdala, the brain’s emotion center, interacts with the hippocampus to boost memory retention.
Studies have shown that emotionally charged events, whether happy or traumatic, are more likely to be remembered. This emotional glue explains why we remember our first love or a significant loss vividly.
The Role of the Amygdala: Your Brain’s Emotional Archivist
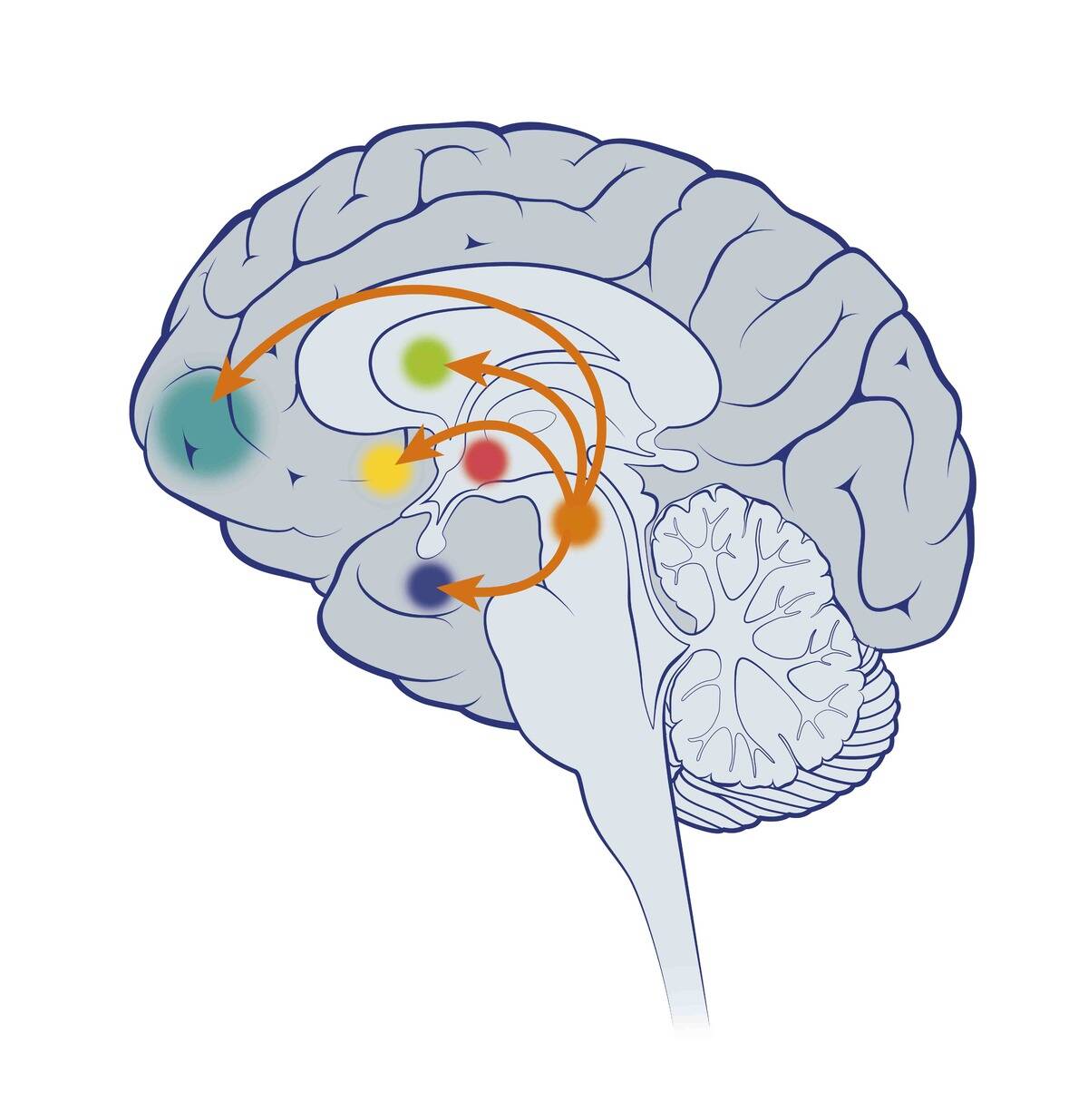
The amygdala is often referred to as the brain’s emotional archivist. It processes emotions and assigns them to memories, making them more vivid. When the amygdala is activated, it can enhance the storage of emotional memories.
This explains why we can recall details from emotionally intense events with clarity. Understanding the amygdala’s role gives us insight into how emotions impact memory retention and why some moments are unforgettable.
Flashbulb Memories: Capturing Moments in Mental Snapshots

Flashbulb memories are vivid, detailed recollections of significant events. These memories are like mental photographs capturing a moment in time. Events like 9/11 or a personal milestone often result in flashbulb memories.
Researchers suggest that the emotional intensity and surprise associated with these events contribute to their vividness. However, while they feel incredibly accurate, studies have shown that these memories can be subject to distortion over time.
The Power of Firsts: Why Initial Experiences Are Unforgettable

First experiences often leave a lasting impression and are more likely to be remembered. This is because our brains are particularly attentive to new information. The “primacy effect” suggests that firsts are more likely to be encoded into long-term memory.
Whether it’s your first day at school or your first kiss, these initial experiences stand out because they are novel and emotionally charged, creating a strong memory trace.
Nostalgia: A Sentimental Journey Through Time

Nostalgia is a powerful emotion that transports us back in time. It often involves reminiscing about past experiences that bring comfort and joy. Studies have shown that nostalgia can enhance mood and increase feelings of social connectedness.
The sentimental value attached to these memories makes them enduring. Interestingly, nostalgia can also serve as a coping mechanism, helping individuals deal with stress and loneliness by connecting them to their roots.
The Von Restorff Effect: Why Unusual Events Stand Out

The Von Restorff Effect explains why distinctive events stand out in our memories. When an event is unusual or different from the norm, it captures our attention and is more likely to be remembered.
This effect highlights the importance of novelty in memory retention. For instance, a surprise party or an unexpected encounter is more likely to stick with us due to its uniqueness, making it easier for our brains to encode and recall.
Hormones and Memory: The Connection Between Stress and Recall

Hormones significantly influence memory, particularly stress hormones like cortisol. While moderate stress can enhance memory by increasing alertness, chronic stress may impair memory formation. Cortisol affects the hippocampus, impacting how memories are stored and retrieved.
This dual role of stress in memory highlights the delicate balance our brains maintain in processing information. Understanding hormone interactions with memory can shed light on why stressful events are sometimes remembered vividly.
Vivid vs. Accurate Memories: Are They Truly Reliable?

Vivid memories feel incredibly real, but they aren’t always accurate. Research shows that people often recall vivid details of an event but may misremember specifics. This discrepancy is due to the reconstructive nature of memory.
Our brains fill in gaps with plausible details, leading to distortions. Despite their vividness, memories can be influenced by subsequent information, highlighting the difference between feeling sure of a memory and its actual accuracy.
The Social Aspect: Sharing Memories and Their Impact

Sharing memories with others plays a crucial role in how they are retained. Social interactions can reinforce memories, making them more vivid and lasting. When we recall and narrate experiences, we often solidify their details.
This process is known as “collaborative recall.” Interestingly, the act of sharing memories can also lead to shared distortions, where people’s recollections influence each other, altering the original memory over time.
The Role of Repetition: Practice Makes Permanent

Repetition is a key factor in memory retention. The more often we recall and use information, the more likely it is to be stored in long-term memory. This principle is evident in practices like studying or rehearsing a skill.
The “spacing effect” suggests that spaced repetition over time enhances memory retention. By revisiting information periodically, we strengthen neural connections, making memories more robust and less susceptible to forgetting.
Cultural Influences: How Society Shapes What We Remember

Culture plays a significant role in shaping our memories. Social norms and traditions influence what we consider important and worth remembering. Collective memories, like national holidays or historical events, are reinforced through cultural narratives.
These shared experiences help create a sense of community and identity. Additionally, different cultures prioritize different types of memories, such as individual achievements or communal events, impacting how memories are formed and recalled.
The Impact of Technology: Digital Memories and Their Longevity

Technology has transformed how we store and recall memories. Digital devices allow us to capture moments and revisit them easily. However, reliance on technology can lead to “digital amnesia,” where we forget information because we know it is stored elsewhere.
While technology offers convenience, it also raises questions about memory longevity. As digital formats change and data becomes obsolete, the permanence of digital memories is uncertain, contrasting with traditional forms of memory storage.
Personal Significance: The Weight of Meaningful Moments

Memories that hold personal significance are often more enduring. When an event aligns with our values or self-identity, it becomes a part of our narrative. The more meaningful an experience, the more likely it is to be remembered.
This is because significant events engage multiple aspects of our cognition, from emotions to reasoning. As a result, moments that resonate deeply with us tend to form lasting memories, shaping our sense of self.
Memory and the Senses: How Sight, Sound, and Smell Play a Role

Our senses play a crucial role in memory formation. Sensory experiences can trigger vivid memories, often referred to as “sensory memories.” The smell of freshly baked cookies can transport us back to childhood, while a particular song might remind us of a specific moment in time.
These associations occur because sensory inputs are processed in the brain’s regions related to memory, highlighting the interconnected nature of our sensory experiences and memory retention.
The Age Factor: How Early Memories Differ from Later Ones

Age influences how we form and retain memories. Early childhood memories, often termed “childhood amnesia,” can be elusive due to the brain’s development. As we age, our memory processes mature, allowing us to form more detailed and lasting memories.
However, older adults may experience a decline in memory retention, often attributed to cognitive changes. Understanding how age affects memory helps explain why certain periods of our lives are more memorable than others.
Tips for Creating Lasting Memories: Making the Most of Every Moment

Creating lasting memories involves actively engaging with experiences. Being present in the moment, capturing memories through journaling or photographs, and sharing them with others can enhance memory retention. Incorporating emotions and sensory details into experiences also makes them more memorable.
Practicing mindfulness and reflection ensures that significant moments are not only experienced but also remembered, allowing us to cherish and recall them long after they have passed.




