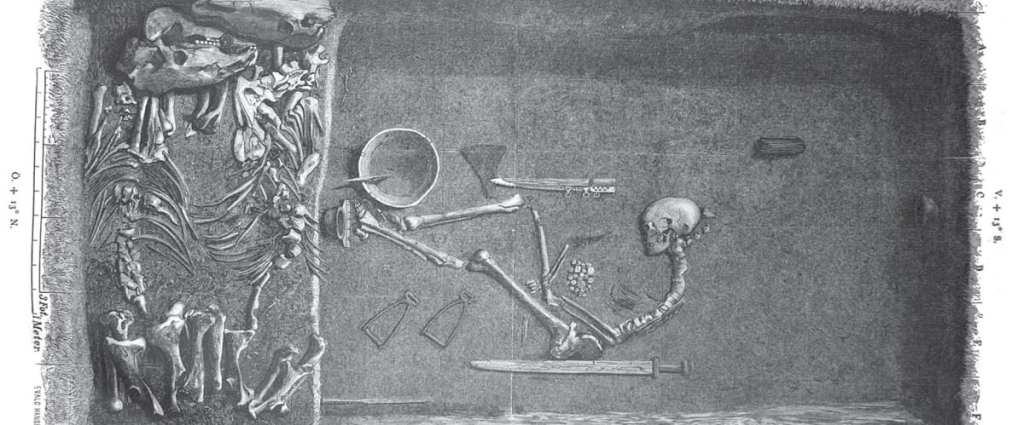In 1878, archaeologists opened a burial chamber in an important Viking trade center known as Birka and found the remains of what they assessed as a high-ranking Viking warrior. The person was buried with their weapons, grand clothes, and two horses. They assumed the remains were male, but back in 2017, a DNA study concluded that the remains were biologically female.

Image Credit: Wikipedia
Critics of the findings argued that the weapons could have belonged to her husband or that there could have been two skeletons in the grave and the analysis was done on the wrong one. They argued that thinking that women were Viking warriors is wishful thinking and that we don’t have enough historical evidence to support the claim.
Researchers, though, are defending their findings in the journal Antiquity, saying the remains buried in the chamber are “unassailably female.” They confirm that there was only one skeleton in the grave, so they couldn’t have mixed up the remains, and asserted that all documentation was correct.

Image Credit: Wikipedia
“Grave Bj.581 had only one human occupant,” confirms Professor Neil Price to IFLScience. “An extra thigh-bone in the Bj.581 museum storage box – much hyped by our online critics – is clearly labeled as coming from another grave and had just been misplaced in the wrong box (the possibility of which is why bones are labeled to begin with!).”
He also continues to make an even finer point:
“To those who do take issue, we suggest that it is not supportable to react only now, when the individual has been shown to be female, without explaining why neither the warrior interpretations nor any supposed source-critical factors were a problem when the person in Bj.581 was believed to be male.”
Ideas about gender, of course, are not set in stone and vary between cultures, so it’s fair to say the skeleton could belong to a person who was both a female and a warrior, and also to accept the fact that being a woman might not have meant the same thing in that culture as it does in ours today.

Image Credit: Wikipedia
Professor Price agrees.
“The body’s XX chromosomes revealed in the genomic study provide an unambiguously female sex determination, but the gender of the Bj.581 individual is a different matter. There is, of course, a broad spectrum of possibilities, many of them involving contested contemporary terminologies that can also be problematic to apply to people of the past.”
The archaeologists on the study expect that, in the future, we’ll probably find more and more Viking Age female warriors, whether they’re new finds or reassessments of remains already catalogued.
The future – and the past – is female, it would seem.